How to Implement an ERP System Effectively
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system can be a complicated task for any organization.
But with careful planning and fulfillment, it can also lead to great improvements in operational efficiency and business performance.
In this article, we will explore the steps involved in implementing an effective ERP system and discuss typical mistakes you can face.
What Is an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) System?
An Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a software solution that combines and manages different business processes into a single system.
It acts as a central storage of information, enabling different departments within a company to share data and effectively work together.
An ERP system unites multiple crucial aspects, such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, and customer relationship management.
By streamlining these diverse processes, an ERP system provides a holistic view of the organization’s operations and enables efficient management of resources.
At its core, an ERP system simplifies the flow of information within different units. This allows for better synchronization and decision-making.

The key features of an ERP system include:
- Centralized Database: An ERP system controls a single centralized database where all relevant data is stored. This ensures data integrity and accuracy and eliminates the need for redundant data entry.
- Integrated Modules: An ERP system consists of various modules catering to different functional areas. These modules are interconnected, allowing for smooth data flow between departments.
- Standardized Processes: An ERP system promotes the standardization of business processes by enforcing predefined workflows and best practices. This increases efficiency, consistency, and improved quality across the organization.
- Real-time Reporting and Analytics: An ERP system gives real-time access to data and offers detailed reports and analytics. This enables staff to make better decisions based on error-free and up-to-date information.
- Improved Collaboration: As a single system, ERP simplifies work and communication between different units. Also, it eliminates data inconsistency and enhances cross-functional cooperation.
- Scalability and Flexibility: An ERP system is designed to adapt to the changing requirements of an organization. It can be customized and scaled as the business grows, ensuring long-term viability and adaptability.
What’s the Purpose of an ERP System?
The primary purpose of an ERP system is to streamline and enhance business processes, improve data accuracy, and help decision-making.
By integrating different functional areas, an ERP system enables organizations to get rid of data inconsistency, reduce manual tasks, and achieve greater efficiency and productivity.
On top of that, an effective ERP system simplifies efficient collaboration and coordination among teams. It ensures that all employees have the most up-to-date and relevant information and can access it at any time.
In addition to integration, an ERP system helps companies optimize resource utilization.
With such features as inventory management, production planning, and supply chain control, an ERP system provides insights into resource availability, utilization, and performance.
By getting visibility into these patterns, organizations can make data-driven decisions to effectively distribute resources, minimize waste, and maximize operational efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP Software
Implementing ERP software can bring numerous benefits to businesses of all sizes. Here are some advantages of ERP systems:
- Streamlined Processes: An ERP system provides a single database that eliminates data redundancy and allows for efficient process automation. It streamlines operations, reduces manual work, and improves overall efficiency.
- Improved Productivity: By automating routine tasks and giving real-time information, ERP systems enable employees to focus on value-added activities. It leads to increased productivity and time savings.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: ERP systems provide many real-time insights. And with accurate and up-to-date data across various departments, managers can quickly make the right decisions.
- Better Collaboration: ERP systems facilitate collaboration and communication across departments by providing a common platform for sharing information, workflows, and documents. It breaks down information silos and promotes cross-functional collaboration.
- Legal Compliance: ERP systems often have features that secure compliance with industry norms and standards. They help organizations meet legal requirements, reduce the risk of penalties, and improve audit readiness.
However, implementing an ERP system also comes with particular challenges and drawbacks, such as:
- Cost: Implementing an ERP system can involve significant upfront costs, including licensing fees, customization, training, and ongoing maintenance expenses. For small and mid-sized businesses, the enormous financial investment can be a huge barrier.
- Complexity: The ERP implementation process is a complex task that requires preparation, resource allocation, and change management. Enterprises must invest time and effort in system configuration, data transfer, and training. And this, in turn, can be pretty expensive and time-consuming.
- Customization Challenges: Customizing an ERP system to align with specific business needs can be a complex and costly venture. It requires deep expertise and technical knowledge to modify the system. And this may result in longer implementation, higher costs, and potential compatibility issues.
- User Resistance and Training: ERP systems often introduce new processes and technologies, which can face resistance from employees accustomed to existing systems. Good training and change management are essential to ensure user acceptance and reap the benefits of the ERP system.
- Dependence on System Reliability: Companies become heavily reliant on the ERP system for their core operations. Any system downtime or technical issues can disrupt business processes and impact performance. It is vital to have reliable emergency and disaster recovery plans to reduce potential risks.
When assessing the potential and benefits of using an ERP system, it is important to consider both advantages and disadvantages.
Organizations should run a thorough analysis and weigh the possible rewards against the associated costs and challenges before starting to use ERP software.
How to Implement a New ERP: 10 Easy Steps
To implement a new ERP system effectively, organizations should follow a structured approach. Here are ten essential steps to consider:
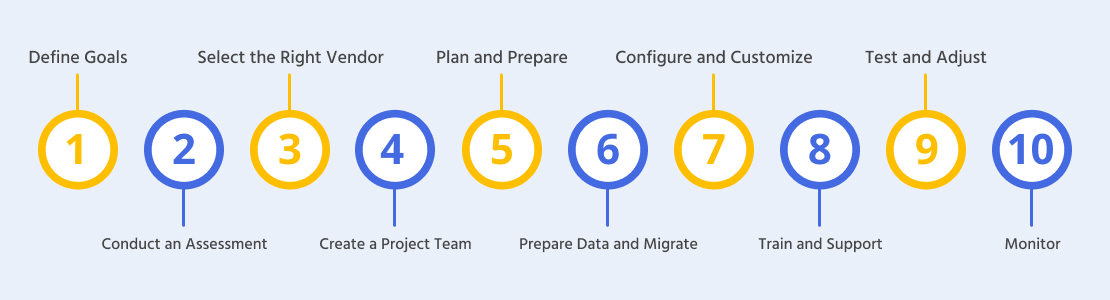
- Define Goals: Clearly define the goals and reasons for the ERP adoption, such as improving efficiency, enhancing reporting capabilities, or standardizing processes.
- Conduct an Assessment: Assess the organization’s requirements, processes, and pain points to determine the functionalities and modules needed in the ERP system.
- Select the Right Vendor: Research and evaluate ERP vendors based on their industry experience, product features, scalability, support services, and cost.
- Create a Project Team: Gather a cross-functional project team consisting of representatives from various units who will be involved in the ERP implementation.
- Plan and Prepare: Develop a comprehensive project plan that outlines the implementation timeline, resource allocation, training requirements, and change management strategies.
- Prepare Data and Migrate: Cleanse and consolidate existing data to ensure its accuracy and compatibility with the new ERP system. Develop a data migration plan and execute it carefully.
- Configure and Customize: Work closely with the ERP vendor to set the system according to the organization’s conditions. Then customize workflows, reports, and dashboards as necessary.
- Train and Support: Provide thorough training to end-users to help them understand the new ERP system, address resistance, and speed up adoption.
- Test and Adjust: Conduct thorough testing with a particular group of users to assert the system’s features, identify any issues, and make necessary adjustments.
- Monitor and Improve: Deploy the ERP system across the organization, closely monitor its performance, and always improve processes based on feedback and user experiences.
By following these ten steps, organizations can implement a new ERP system effectively, minimizing disruptions and maximizing the benefits it brings.
Each step plays a crucial role in ensuring a successful implementation that aligns with organizational goals and drives long-term growth.
Remember that ERP implementation is an ongoing process, and continuous improvement is essential to leverage the full potential of the system.
How to Implement an ERP System: Common Mistakes to Avoid
If you want to implement an ERP system, you should be aware of common pitfalls to ensure a successful implementation.
Some mistakes to avoid include the following:
- Insufficient Planning: Inadequate planning can lead to delays, cost overruns, and poor system adoption. Take your time to work out a quality plan and involve key participants in the process.
- Lack of Top Management Support: Without strong support from top management, ERP implementation may not receive the necessary resources, commitment, and authority. Secure executive sponsorship to ensure a smooth application.
- Poor Change Management: Neglecting change management can result in employee resistance, poor adoption, and project failure. Develop a reliable change management strategy that includes communication, training, and response to concerns.
- Overlooking Data Quality: Failing to address data quality issues before migration can result in inaccurate or incomplete data in the new ERP system. Invest resources in data cleansing and checking to ensure reliable information.
- Excessive Customization: While customization is necessary to align the ERP system with specific business needs, excessive customization can lead to higher costs, extended implementation time, and compatibility issues during upgrades.
- Insufficient Testing: Inadequate testing can lead to system errors, data inconsistencies, and disruptions to business operations. Conduct comprehensive testing to find and settle any issues before the release stage.
- Inadequate Training: Insufficient training can block user adoption and impede the system’s effectiveness. Provide all-round training to users at all levels, highlighting the system’s benefits and responding to their concerns.
Bottom Line
Building an ERP system requires good preparation, careful assessment, and proactive management of challenges.
While it can bring significant improvements in operational efficiency and business performance, organizations should consider both the advantages and disadvantages before proceeding to the implementation process.
By following a structured approach, selecting the right vendor, and prioritizing change management and user training, organizations can maximize the benefits of an ERP system while avoiding common pitfalls.
An experienced SCAND team is ready to help you with implementing the ERP system: choosing the one that suits your needs, integrating and maintaining it, and also training your employees.













