Modern software development relies on speed. Waterfall’s monolithic all-or-nothing approach has been mostly displaced by quick iterative practices that facilitate development and deployment – continuous integration (CI), continuous delivery (CD), and continuous deployment(CD).

While each practice has its own advantages, the common emphasis on continuous iteration has transformed the essence of software development. Companies can deliver software to the market faster, test new features more efficiently while lowering risk and cost.
This type of iteration relies on thorough planning and active pipelines that support multiple iterations at different phases of the development cycle, keeping the entire development team involved. While one build is deployed, the next is being tested, and the new build in the cycle is being coded.
If you’re in an IT-related business, knowing how to use the CI/CD pipeline is crucial to keep your company competitive. Here is what you need to know about CI/CD practices and why they matter.
What Is CI/CD Pipeline?
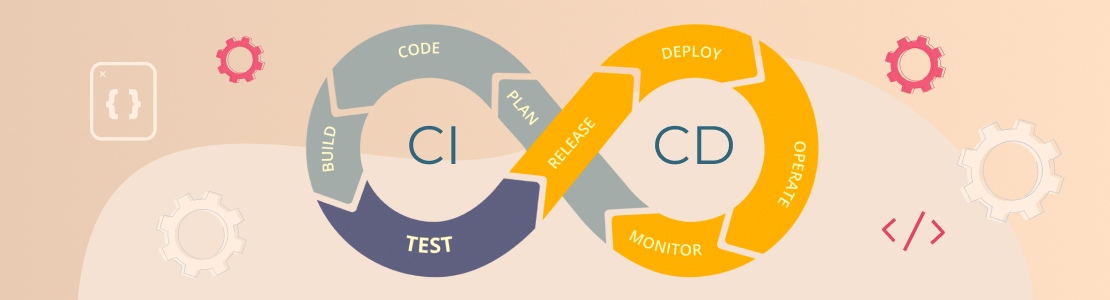
“CI/CD” stands for the combined practices of Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD).
It’s a software development approach that allows you to deliver upgrades at any time and in a sustainable manner. Development cycles are more frequent, impactful, and faster when code changes are routine.
In CI, developers merge code changes in a central repository multiple times a day. The goal is to create a deployable artifact. CD adds the practice of automating the entire software release process. Automated tests are used to ensure that the artifact for a given version of code is safe to deploy.
In Continuous Delivery, code changes are also continuously deployed, although the deployments are initiated manually. Most teams work in environments other than production, such as development and testing, and CD ensures that code changes are automatically pushed to those environments. If the entire process of moving code from source repository to production is fully automated, the process is called Continuous Deployment.
Benefits of CI/CD Pipeline
CI/CD is more than just task automation to avoid human mistakes. It allows companies to deliver innovative solutions to users as quickly and efficiently as possible.
- Better collaboration and quality. The rationale behind CI/CD pipeline is that it is easier to find bugs on smaller code differentials rather than larger ones that have been produced over a long period of time. Furthermore, when developers work on shorter commit cycles, they are less likely to be editing the same code at the same time.
- Improved stability and fewer bugs. The CI/CD pipeline allows building code simultaneously, lowering the risk of a build failure. It’s easier to isolate and eradicate bugs with smaller releases and automated test cycles. Teams can also utilize feature flags without having to use code to easily disable specific functionality that isn’t ready or can cause an unforeseen problem.
- Software delivery with less risk. Pipelines for continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) standardize release processes across projects. You limit the chances of creating bugs by testing every change in source code.
- Frequent release of new features. A CI/CD pipeline can visualize the whole path from commit to production in a single screen, allowing you to navigate across stages, identify inefficiencies, and improve the workflow. By eliminating the roadblocks to efficiency, you lead your product to success.
- A product that users need. Frequent updates often mean more feedback from users. A/B testing features or testing early versions of products with real customers are two ways to take advantage of this. This way, you can avoid wasting resources on features that your customers don’t need and instead focus on the ones they do.
- Increased productivity. Developers that don’t use CI/CD are frequently under stress because of recurring bad deployments and difficult-to-fix outages. Because long-lived feature branches are too large to receive a proper review, code quality suffers. CI/CD, on the other hand, helps product managers optimize for user impact. Code is deployed while it is still fresh which leads to h the development of better products.
- Reduced costs and easier maintenance. DevOps teams can maintain and update applications more easily. Automation eliminates the need for manual requests or unnecessary back-and-forth between developers and operations teams, as well as streamlines testing and decreases the number of errors that can occur in many of the recurring processes of the SDLC. The CI/CD pipeline helps companies to save costs by updating small batches of code instead of larger software releases, allowing for more scalable and sustainable updates.
CI/CD Stages
A CI/CD pipeline is a specification of the procedures that any software developer must follow to provide a new version of a product. Developers would still have to complete these stages manually if there was no automated pipeline, which would be significantly less productive.
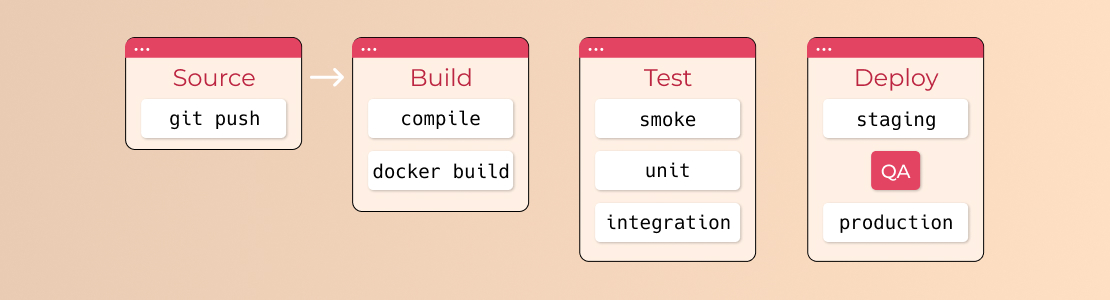
Most software releases go through a couple of typical stages:
Failure in each stage usually triggers a notification to the responsible developers. Otherwise, the whole team receives a notification after each successful deployment to production.
Source Stage
A pipeline run is usually triggered by a source code repository.
When the code is changed, the CI/CD tool receives a notification and runs the corresponding pipeline. Other frequent triggers include workflows that are automatically scheduled or initiated by the user, as well as the results of other pipelines.
Build Stage
The source code is combined with its dependencies to create a functional version of the product that may be potentially delivered to users. The compilation is required for software written in languages like Java, C/C++, or Go, whereas Ruby, Python, and JavaScript do not require this step.
Cloud-native software is generally deployed with Docker, hence this stage of the CI/CD pipeline creates Docker containers.
Failure to pass the build stage signals a major problem with a project’s configuration, which should be addressed as soon as possible.
Test Stage
During this stage, the team conducts automated tests to ensure that the code is correct and the product performs as expected. The test stage serves as a safety net, preventing end-users from being exposed to bugs.
It is the developers’ obligation to write tests. Writing new code in test- or behavior-driven development is the best way to write automated tests.
This phase can take anywhere from seconds to hours, depending on the project’s size and complexity. Many large-scale projects have numerous levels of testing, ranging from smoke tests to end-to-end integration tests that evaluate the entire system from the user’s perspective. To reduce execution time, a large test suite is usually parallelized.
The test stage helps to reveal bugs that the developers were unaware of when the code was written. It’s critical at this point to provide developers with feedback as soon as possible, while the issue is still fresh so it will be easier to fix it.
Deploy Stage
This is the final stage of the process, during which the product is made publicly available. The build is ready to deploy to a live server once it has completed all of the relevant test cases.
How CI/CD Pipelines Help Development Teams
Imagine having to coordinate teams every time you need to run a test suite or set up the infrastructure for the next environment. This would result in fewer iterations and longer source and build stages.

The CI/CD pipeline is the pathway for getting the code into production. Software development is an iterative process, and developers can run automated CI/CD pipelines without the need for human interaction.
One of the main goals of DevOps teams is to foster the learnability and usability of pipelines. Certain environment-driven pipelines may let developers run all the way through pre-production while requiring another pipeline to reach production environments. This would require a lot of iteration until the development team is satisfied with the pipeline. Fully automated CI/CD pipelines would go one step further and automate the process all the way to production.
Conclusion
The majority of monolithic approaches to software development are no longer effective in up-to-date ever-changing requirements and user expectations. Businesses have to quickly react to user feedback and adjust the development process accordingly. That’s where quick iterative practices can come into place – continuous integration (CI), continuous delivery (CD), and continuous deployment(CD).
CI and CD provide more agility by decreasing software development and delivery timeframes from months to weeks or even days. This enables companies to produce better software more efficiently and within a shorter time frame.
SCAND DevOps team is using CI/CD principles to offer seamless system development and update with zero downtime. If you need assistance with implementing CI/CD principles into your development process, feel free to contact us.












