The Role of Smart Contracts in the Government Sector
The adoption of new digital technologies is quickly happening in all spheres. Industries and governments seek ways to streamline, automate, and make cheaper routine operations while providing a whole new level of client service. One of the recent innovations that are predicted to disrupt many industries and enhance productivity is blockchain.
Businesses from various industry domains are leveraging blockchain technology to build new more secure, flexible, and cost-effective structures, and government and public sectors are no exception. By using blockchain and smart contracts, governments can significantly decrease silos between their entities and build decentralized highly transparent and agile systems.
In this article, you’ll find out what are smart contracts in blockchain technology, and how smart contracts can be practically implemented by the government and public sectors.
What Is a Smart Contract In Blockchain?
A smart contract is a small program based on blockchain that is used to establish certain conditions or agreements between participants. When the preprogrammed parameters are met, blockchain contracts execute themselves automatically and the agreement is considered fulfilled.
Smart contracts can be used as enhanced traditional contracts. Apart from legislation they also rely on computer code and get enforced automatically, achieving greater reliability and implementation of the law. For example, insurance companies use these contracts to provide insurance payments when certain events like floods or flight delays, and others happen. This way, they manage to minimize any possible errors when paying to a large number of clients while ensuring quick payouts without any delays.
As smart contracts get executed on the blockchain, they gain the advantageous properties of this technology, including:
- enhanced security – to secure contracts software developers use cryptography; it helps to prevent any altering in records as well as any hacker attacks, e.g. unauthorized funds withdrawal, spoofing, contract replacement, and others;
- transparency – blockchain is a public ledger that keeps all the records of transactions made between the participants visual in the network; any user in the blockchain can see which contracts were executed; meanwhile, the nodes can stay anonymous in the network;
- exclusion of intermediaries – there is no need for a middleman to verify the process of agreement fulfillment; therefore, the process becomes much faster and cheaper;
- instant operation – the contracts get executed instantly as soon as the included conditions are met;
- decentralization and autonomy – smart contract operations avoid the necessity of human intervention; this way, the parties involved don’t have to wait, control, or “push the button” for the operations to be executed;
- accuracy – the contracts written in code require precise language and exclude any uncertainty or ambiguity; therefore, the parties can’t unfairly interpret the agreement content to their advantage as well as change or amend it;
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart contract operations don’t differ much from blockchain transfers. When initiated and executed smart contracts undergo the following steps:
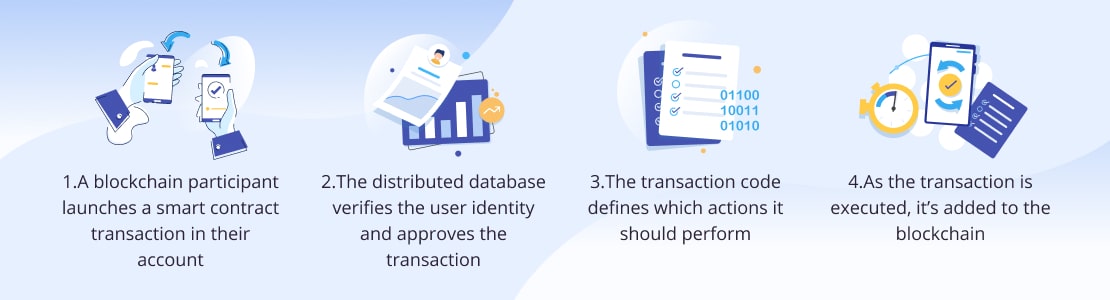
Smart contract conditions are based on simple logics of IF-THEN or WHEN-THEN statements recorded as code on a blockchain. The actions encoded into smart contracts can include vehicle or land registry, payment services, money transactions, and much more. When creating a smart contract, apart from “if/when – then” statements, the parties also have to determine:
- how the transactions should be performed;
- what data to include in the transactions;
- if there are any exceptions;
- the ways to resolve the disputes.
Businesses use various apps with special tools and templates to facilitate the process of smart contract creation. These apps help connect legal aspects of an agreement to the computer code, ensuring its legally-enforceable foundation.
Benefits of Blockchain and Smart Contracts in the Government and Public Sectors
There is a wide range of ways governments can leverage public ledger for streamlining processes to fraud reduction, to resource sharing, to secure data storage. Let’s have a look at some examples of smart contracts and blockchain usage in government and public sectors:
Identity Management
With global digitization, people express more concern about their digital private data. With blockchain, governments can establish well-protected digital identities of their citizens, gathering all the private data, e.g. birth certificates, passports, marriage licenses, driving licenses, etc. into a single encrypted element. Personal records can be changed or managed with the help of smart contracts and data access can be provided with individual authorization.
In the future, digital identities are likely to be extended with more data, e.g. health records and voting rights, making data access more convenient and controlled by individuals.
Taxation
Tax authorities can significantly speed up and streamline tax collection processes with smart contracts. The contracts can be used for checking if tax data matches with the transactions made or calculating social security and tax deductions.
Aside from verifying tax data compliance, implementing a public ledger, tax departments can decrease the cases of tax fraud.

Vaccine Tracking
The Covid-19 outbreak has presented new challenges to the world. Part of them can be successfully solved with blockchain and smart contracts. For example, the vaccine passports can be enhanced with blockchain vaccination verification systems to quickly verify the vaccination status of citizens. Meanwhile, embedded into vaccine distribution networks, blockchain can ensure vaccine safety and efficiency as well as provide real-time visibility of its distribution.
Public or Private Networks
Governments can use blockchain for public and private access. When used publicly, anyone can access the network and participate in it. For example, citizens can provide their data through the ledger and get identical copies of the documents, e.g. licenses or certificates. This way, governmental institutions, and citizens can quickly exchange the data and guarantee that it doesn’t get lost anywhere.
Private blockchain networks are used for permissioned data access. The governmental facilities can use this type of network for inner data exchange. Moreover, each organization can be authorized to have access only to specific data or get limited access to the ledger depending on the given rights.
Bottom Line
Blockchain and smart contracts have a disruptive potential for many industries. Nevertheless, we’re only discovering how it can be implemented in various spheres. Businesses were the first to experiment with the technology and today it’s effectively used by many to keep the competitive edge in the market and enhance customer service and data security.
Now, ledger technology is becoming more common in governmental and public sectors. Governments search for ways to speed up, streamline, and make more transparent their document operations, fund transactions, and public relationships, and a smart contract development company can provide the solution to many of them.














