How to Build a Personal Finance App: The Complete Guide
Let’s start from the heart: on the eve of 2025, the value of personal finance tools, especially in banking and financial services, is tremendous. Personal financial software has immensely influenced our everyday routines.
Given that the app is placed on your smartphone, users can easily track and control their spending right on the spot, plan their budget, and have reminders about important payments or shopping gifts.
Besides, personal finance tools offer much more: users can control expenses, manage risks, raise funds, expose credits and loans, and secure insurance—on paper and electronic tools.
In this article, we’ll uncover the technical intricacies of the personal finance app development process, and clear up the costs and challenges on the way.
Hop on our tips and extra information to guide you along the way. Whether you choose the professional software developer team or tackle this challenge on your own, with all the necessary information in your pocket the task won’t be hard. Good luck on the way!
What is a Personal Finance App?
Personal finance apps are like personal caregivers that contribute to users’ financial and mental health. These are applications that allow you to throw out all the old-school devices and assist you with budgeting, spending, and investment records on paper and electronic devices.
In our highly technological era, when every step is actually processed in the digital domain and assisted by AI and machine learning, the decision to develop a personal finance app for your business seems clear and logical.
Since there’s a huge demand for personal finance apps, let’s look at some stats to gain a better perspective on personal finance app development.
According to the TEM journal study ‘Personal Finance Management Application’ of August 2024, modern households increasingly need help in assisting them track their income and daily expenses, investing funds, planning budgets, and building and structuring their financial strategies.
The remote solution for taking full control over a client’s money is a huge step towards financial independence. It offers new opportunities for growth, both in personal and business domains, showing up as a major boost in business expansion and conquering the market.
As for the Future Data Stats, the projection of the global personal finance management applications market is to grow from $1.23 billion in 2023 to $1.61 billion by 2030. Thus, creating personal financial software will be an outstanding business impetus.
Personal Money Management Software: Generation Trends in Building Personal Finance Apps
The scientific research on personal finance app development in the Journal of Economic Education and Entrepreneurship Studies shows—there is great potential for scaling your personal finance app development business among Gen Y.
Utilizing personal finance apps to track expenditures, form family budgets, and carry financial deals allows users, specifically Millenials, to craft their personal experiences by performing tens of tasks simultaneously, based on their active needs and multiple financial demands.
Following the paper ‘Fintech Analysis of Personal Finance App Usage among Millennials’, data security and personal privacy are the Millennials’ key concerns while using fintech apps. Their crucial priority is personal data security and user privacy. For developer teams, a great deal will be staking on enhancing and upgrading security systems and privacy practices.
Who are the next generation users, Gen Z? For developers and businesses, it’s useful to see the stats on this gen’s motivation.
Considering the swift changes in the financial landscape in recent years, fintech companies and banks, including personal financial planning software and personal finance app development, Zoomers are more active users of mobile technologies.
According to the ‘Digital finance and the perspective of Gen_Z cohort: a review’ study, Gen-Z plays a crucial role in the success of personal financial software and makes up a considerable share of the customer base for banks and fintechs.
In the array of their priorities are inclusion, security, and accessibility of financial services. Hereby, for business owners, it means additional concerns to keep in mind while developing the personal finance app.
As you see, together with Gen Y, Zoomers are one of the top consumer generations taking the lead in personal finance app development globally down the road.
Tech Feature Trends in Personal Finance App Development
Now, to keep track of the needs and priorities of potential customers of your personal finance app, it will be a good point to see the tech trends around personal financial software development. This will help you to build a solution that meets the demands of future users.
Due to the rise in optimizing work and free time, the personal apps domain is also transforming to comply with new trends:
- AI and machine learning
- Virtual assistance bots and chatbots
- Open banking solutions integration
- Blockchain technologies
- Gamification
- User-centric user interface
Types of Personal Finance Apps
When it comes to managing your finances, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Personal finance apps come in different forms, each designed to cater to specific needs and goals.
Online Payment Services
Choosing to build your app in this domain brings along a great deal of competing companies. It’s wise for you users to invest in creating this type of personal finance software. At the moment, banks still lack flexibility and mobility in processing payments, so you can have a competitive edge in this field.
Online Banking
Deciding to build this kind of personal finance app could be a beneficial choice, especially now as banks and financial enterprises deliver their services in the digital field. It means personal web and mobile finance apps will dominate the software market.
Crypto Wallets and Crypto Platforms
As seen from the research, cryptocurrency is changing the financial world on a global scale. This way, some companies and customers prefer making and having payments in cryptocurrencies. So, you won’t make a mistake by choosing the crypto wallet to create your personal money management software.
Insurance Tech
This technology includes digital insurance companies and a tech stack featuring AI, Blockchain, Big Data, and more to offer clients improved insurance services.
The Best Apps on the Market to Follow
To catch a clear visual understanding of what a personal finance app is, look at some of the top-notch players in the personal finance software field and consider adopting their functionality.
- Mint: This is the best free app to track your budget.
- Prism Finance: Pay Bills, Money Tracker: This app extends the general personal finance app functionality. You can sync your app with a large number of billing providers.
- Spendee: Taking track of this tool’s features is one of the best options to manage your family’s shared expenses, as in the case of a household.
- EveryDollar: It is one of the most comprehensive apps for budgeting and tracking your spending.
Here are more personal finance software apps to keep your eye on:
- PocketGuard: Budget Tracker
- NerdWallet: Manage Your Money
- Every Dollar: Budget Tracker
- GoodBudget: Budget and Finance
- Mobills: Budget Planner
- Budget Planner: Expense Tracker
Steps to Building a Personal Finance App
Now, given there are plenty of gains and profits for your client or your software company when building personal financial software, it’s time to get into the process of development. Let’s unlock the full potential of the step-by-step approach to creating a personal finance app.
1. Visualize Your App’s Consumer
Getting right to the heart of your target audience guarantees you build an effective and user-centered personal finance tool. It will help your clients reach their goals while protecting their personal data. So, research the topic and detail up the demography.
Also, focus on your user’s needs, habits, geography, etc. as soon as you want to score the bullseye and get results from the release.
2. Dive into the Competitors’ Area
Next, dive into the competition area. What companies are you competing with, and what personal finance app features do they deliver? This is an important survey into the most in-demand functionalities by your future users, and also to think on which features you can improve and reach new heights in the domain.
3. Define the Main Challenge to Tackle
Then, research the optimal technologies to apply in your personal finance app. Consider the tech stack and databases making the UX more steady and comfortable.
4. Security Priority
As mentioned, for the most active personal finance app users—Gen Y and Gen Z—privacy and personal data security are a top priority.
So, consider choosing these practices to make your users’ security even better:
- Apply two-factor authentication. It empowers user verification via two steps of identification, crafting a more protected user experience.
- Cut each session’s longevity to a certain time limit.
- Implement Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard and General Data Protection Regulation.
- Stay away from making your users’ personal information clearly visualized, especially in public spots. No bright color palette and no catchy fonts are recommended.
5. Choose Your Personal Finance App Basic Features
Initiate the development process with the basic personal finance app components. Consider the following:
- User authorization to shield users from information leaks.
- The user profile to add and revise basic personal info.
- Income and expense management to watch over money transfers in real time.
- Reminders and notifications about future and potential payments, statistics on payments and spending, and significant updates.
- User registration and onboarding to make the app accessible only to authorized users via secure login registration.
Moreover, you can enrich your personal finance app with add-up services like AI chatbots, external bank accounts, calculations, barcode scanning, and much more.
6. Pick Optimal Technologies and Databases
Talking about the tech stack, consider relevant programming languages, databases, and frameworks that are compatible with specific programming languages applied.
- Front-end application technologies build up a visual and tangible interaction with the user. Usually, this stack includes HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- The backend forms the core structure of your app and is in charge of optimal data loading, data protection, and the convenience of money transfer. It relies on languages like Ruby, C++, Python, Kotlin, or Node.js.
- Database solutions should be safe and respond promptly to user queries. Consider options like MongoDB, Express.js, Node.js, or Angular.
- If you are building a rich-in-features personal finance app, think about including API integrations.
7. Easy-to-Use UX
Technologies for using a personal finance app conveniently and safely are highly important. So, a responsive and easy-to-understand user experience (UX), together with a smooth user interface (UI), will drive your app to the top.
However, remember about security and avoid extremely bright fonts and colors. The contrast in shades and colors should be your UI priority.
Besides, try not to overwhelm your users with too much information on one screen and distribute information in a uniform way.
8. Testing and Quality Assurance
This is the stage definitely not to skip. Whenever users’ data in your personal finance app is lost or compromised, all the previous work goes in vain.
So, put your best efforts into testing and assuring quality checks on all the development stages: security testing, data integrity, usability, functional and performance testing. Alternatively, hire a professional QA team.
When you have checked all the bugs and shortcomings, the application can be published in the app stores.
Must-Have Features for a Personal Finance App
Let’s have a look at the most popular personal finance applications: Mint (free, with optional paid upgrade), NerdWallet (free), Buxfer (free, paid plans), Goodbudget (free, paid plans), Every Dollar, Mobills (free, with optional paid updates), with personal finance apps bragging free versions—Prims, Spendee, and Budget Planner.
Some of these apps offer free trial versions, some do not. Yet, for scaling and promoting your personal finance app, the possibility for current and potential customers to download your software product quickly and with no extra expenses has a good potential.
Take the top personal finance app, Mint, which is free and has conquered the world due to its no-expenses option, just with additional non-binding updates. As with most personal finance apps, it’s synchronized with the bank and is easy to use.
Below are the most in-demand personal finance app features built into most of the popular apps:
- User registration and onboarding that make the app accessible only for authorized users via secure login registration
- Account integration with multiple financial services
- Managing personal budget
- Receiving a financial status report for a certain period
- Insightful advice via AI chatbots
- Getting extensive expenses and income reports
- Currency converter
- Extraction of charts
- Portable calculator
- Report generation and visualization through charts
- Barcode scanning preview
What’s more, remember about the security and data privacy tools as these will remain the highest priority for your users. It is a challenge to keep in mind for a business owner.
Main Points to Consider While Building a Personal Finance App
So, in creating a personal financial app, you need to consider the following points to ensure your app’s success.
1. Project Features
If your customer wants third-party APIs integrated, it’ll take longer to launch, and the tech stack will become much more complex to protect users’ personal data. It means more than one programming language, enhanced synchronization, more versatile screens, API integrations, and tailor-made UI.
2. Time to Market
The general equation is that the longer the project development time, the more expensive it will be. In the case you’re restricted in time, put your eye on ready-to-go software solutions. For instance, to benefit from code reuse and simple support, choose the combination of Python programming language and Django framework. On the contrary, if there’s plenty of time ahead to work on your personal finance app, seize the opportunity to develop a more features-packed app, using the Java language and Spring framework.
3. Personal Data Security
The point here is to shield the personal financial software system through protected libraries and frameworks resistant to cyber threats and hacking attacks, that would also be compatible with industry standards like CBDP, and PCI DSS.
4. Product Architecture
Now, if you or your client wants to maintain scalability and third-party integration capabilities in this personal financial instrument, it will be more profitable to bet on microservices architecture. So, a programming language like Ruby is needed to incorporate into your personal financial software stack—to cope with large numbers of simultaneous users.
Tech Stack and APIs for Personal Finance Apps: Scalability Potential
As we embark on selecting the relevant software technologies for your personal finance app development, keep in mind the most crucial challenges in —security and performance.

From this perspective, here’s the list of the most relevant technologies for your personal accounting app project:
1. Front-End Technologies for Your Personal Finance App
- React Native: Enables cross-platform app development, allowing the same code to run on both iOS and Android devices. It reduces development time and costs while maintaining high performance and a native look and feel.
- Databases: MongoDB, Express.js, Node.js, Angular. For clients wanting a scalable cross-platform financial app, they would be a great choice.
2. Back-End Technologies
- Python programming language is a popular technology for simplicity and open-source frameworks like Django and Flask. This choice provides your personal finance app project with flexibility and robust measures. The language is also well-adapted to investment and AI trades.
- Java language comes up as a relevant choice if you need an enhanced environment for the app. Its Spring framework backs up enterprise-level projects with scalability options.
- Kotlin and Node.js are a good pick for creating real-time personal finance apps (e.g., banking apps) leaving the possibility for many simultaneous connections.
3. Database Technologies
- SQL Databases (MySQL or PostgreSQL) will give your application data integrity and reliability, and empower the app with the possibility to structure data and transactions.
- NoSQL Databases. On the contrary, Cassandra and MongoDB databases allow you to scale the functionality of your personal finance application horizontally and change it as needed.
4. Mobile Development
- React Native: A go-to framework for building apps that work on both Androids and iPhones with one codebase.
- Flutter: Google’s toolkit for creating high-performance apps for mobile, web, and desktop, all from a single codebase with appealing designs.
- Ionic: A flexible, open-source framework using web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) to make sleek, cross-platform apps.
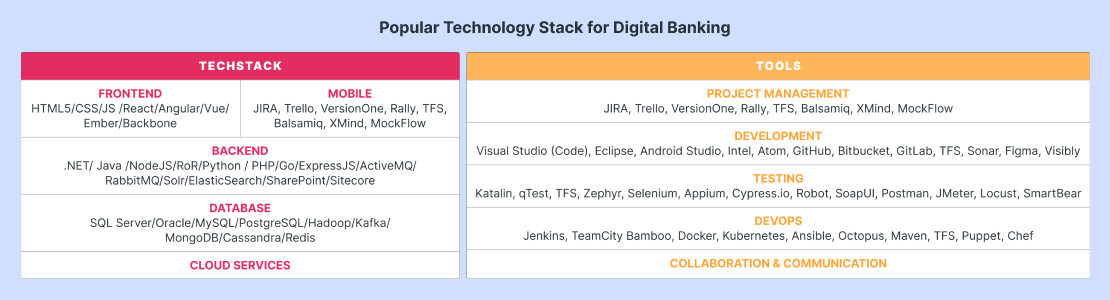
5. APIs
As for the list of APIs to build your personal finance software, it will be based on the geographic location of your partner bank and the technical complexity of your personal finance application.
Generally, the app’s users are in charge of unclosing their personal information, which helps your finance app examine the user’s data and enhance the productivity of the tool.
Cost of Building a Personal Finance App
When you understand the technology behind creating personal financial planning software, the next step is to find out how long it takes to develop a personal finance app.
The answer can’t be straightforward as there are many factors to bear in mind. The expenses for the development of a personal finance app usually start from $37,500. This budget line can fluctuate between $25,000 and $50,000. The final price of a personal finance app depends on:
- App functionality and complexity of features
- What mobile platforms and devices your app will function on
- Third-party integration points
- UI/UX integration
- Smartphone hardware features: GPS navigation, AR and NFC technologies, and more
- Maintenance plan
Apps development fluctuates depending on the team location, your personal finance app tech stack involved, its functionality, and advanced features incorporated in the product on personal financial software planning.
So, let’s see the rates per hour in different regions: USA – $70-150, Canada – $60-120, Western Europe – $65-130, United Kingdom – $45-100, Eastern Europe – $30-65, India – $20-50.
Also, keep in mind the possibility of an MVP creation, if you want to test only the basic features of your personal financial software product on first users and get valuable feedback without wasting resources on enriched app functionality. The cost of this product may vary from $22,500 to $27,500.
Advanced features to include:
- Tailored alerts to suit your client or your project needs ($30-100)
- Integrating the app with banks and financial institutions ($200-300)
- Calculating debts payoff ($50-150)
- Tax control ($100-150)
- Planning retirement tools ($100-300)
- Investment analysis tools ($100-300)
As a rule, software development companies include contingency costs in their project budget. Also, remember about the constant maintenance and updating of the released app in the long view.
How Long Does It Take to Build a Personal Finance App?
It’s clear enough that the time for building each feature in a personal finance app can vary depending on the client demands for the app, the features’ complexity, and the technologies involved, but a lower bound line for basic features is the following:
- Budgeting – 50-150 hrs
- Tracking the spending – 50-100 hrs
- Reminders on bills – 30-100 hrs
- Security – 100-300 hrs
- Goal setting – 50-150 hrs
If we take a generalized time schedule, the pure app development process takes around 470 hours. Yet, in the case of building an MVP or a highly upgraded features stack, a personal finance app cost will shift from 470 to 800 hours.
How to Ensure App Security: Optimised Principles for Personal Finance Apps Security
Keeping your personal finance app secure is super important, especially when it comes to protecting sensitive financial info. We can divide the best security practices into blocks according to functionality:
- User security principles: privacy and user consent, secure authentication and authorization.
- Secure design principles.
- Practices of education on user security: constant security education and training of users. Compliance with regulatory standards, ongoing updates and patch management, testing, and auditing security practices.
- Data minimization and encryption, managing third-party risks, protected storage, and transmission of data.
- Monitoring and log management, regular security assessments, and reviews.
Final Word: SCAND’s Expertise in Fintech App Development
Lost in the turbulent ocean of software development? Don’t know what to pick? You may take note of the advice, and the personal finance tools and technologies provided in the article. This will help clear up your mind about the process of your personal finance app development.
Another way of making a proper decision is to stick to long-standing professionals in the market who adhere to quality and user convenience. So, gain valuable insights into SCAND’s full expertise in personal software development.
With a need to build a personal finance app tailored to your company’s demands, a digital banking service, or a fintech payment solution, the company holds on to the top software development standards.
In a high-demand security domain like fintech software development services, SCAND stands out from the crowd. SCAND’s innovative turn-key and custom-made solutions bring individuals and corporate clients exceptional privacy protection and security.
Moreover, with 20+ years in the mobile and desktop development domain, we turn the use of SCAND products into a comfortable and well-protected user experience.

















