Native vs. Cross-Platform Mobile App Development: Making the Right Choice
If you ever thought of creating a mobile app, you were most likely facing a question of which technology or language to choose for its development.
Apart from native mobile app development, you’ve probably heard of hybrid and cross-platform mobile development. Both methods have their pros and cons, and the suitable choice depends on different factors.
In this article, we will discuss native and cross-platform mobile app development, explain the benefits of both directions, and help you make the optimal decision for your project.
What Is a Native Mobile App?
A native mobile application refers to a software application designed intentionally for a single operating system. In the case of smartphones, the primary contenders are iOS and Android.
iOS Native Development
iOS apps are typically developed using Swift or Objective-C programming languages. Swift is Apple’s latest and preferred language for iOS app development. Objective-C, a bit outdated language, is still used in some existing projects.
Android Native Development
Android apps are primarily written in Java or Kotlin. Kotlin, introduced by JetBrains, has gained popularity for its conciseness, expressiveness, and compatibility with Java.
The Advantages of Native App Development
One of the greatest advantages of native app development is performance. Native apps are optimized for the specific hardware and software of the target device and make full use of the device’s features.
This involves using platform-specific design elements, accessing device sensors, and interacting with other apps on the device.
Native development offers a high degree of customization and integration with the operating system, allowing users to enjoy a consistent and holistic experience.
What Is a Cross-Platform Mobile Application?
Cross-platform mobile applications, on the other hand, are designed to work on multiple platforms, typically iOS and Android, using the same codebase. Developers write the code once and use it across different platforms.

As the development tools, they use frameworks like React Native, Flutter, or Xamarin that help them build cross-platform apps more efficiently.
The Advantages of Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-platform development implies the creation of a single code that can be reused across multiple platforms. This is actually the first benefit of such an approach to mobile development — the reusable code.
One more advantage to mention here is the simplicity of changes and updates: make a change only once, and it will be synced across all the devices regardless of the platform that powers them.
The second significant benefit is the cost. Since there is no need to hire two teams of software developers (for iOS and Android apps), the business can save approximately half of the budget on app development.
The next advantage follows from the first one and relates to the second: time-to-market. Only one code has to be written, which significantly cuts down the time for the development.
There is still an important feature to mention. Cross-platform development eliminates the need to dig into specific languages, as it is enough for the developers to be proficient only in several widely used technologies, for example, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Let’s take a closer look at the top most popular frameworks for cross-platform development: Cordova/PhoneGap, Xamarin, React Native, Flutter, and Ionic.
The Difference Between Cross-Platform and Native App Development
Both native and cross-platform apps are good enough for mobile app development. However, everything depends on the requirements, business goals, and objectives. Let’s delve into the key differences between cross-platform and native app development to help you make an informed choice.
Native App Development
Native app development is a great development approach to get top performance and a customized user experience on each operating system.
Platform Specificity
Creating native apps means making applications specifically for a particular operating system. For example, iOS apps are made with Swift or Objective-C, and Android apps use Java or Kotlin. This specificity lets developers fully optimize performance and use exclusive features of each mobile app platform.
Better Performance
One key benefit of native development is better performance. Code written in platform-native languages like Swift or Java can fully use the device’s capabilities, leading to quicker load times, smoother animations, and a more responsive user experience.
Access to Device Features
Native apps have unmatched access to device features. Developers can easily incorporate features like GPS, camera, sensors, and more, giving users a rich and immersive experience that matches the unique capabilities of their devices.
Cross-Platform App Development
Cross-platform development uses frameworks that let developers create apps for different operating systems, saving time and costs.
Code Reusability
Cross-platform development means writing code once and using it on various app development platforms. This approach is achieved through frameworks like React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin. Reusing code cuts down on development time and costs because developers don’t have to create separate code for iOS and Android.
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Creating one codebase for multiple platforms simplifies development, making it more efficient and cost-effective. Updates and maintenance become easier as changes can be applied universally.
Consistent User Experience
Cross-platform development ensures a consistent user experience on various devices and operating systems. This consistency is beneficial for maintaining a cohesive brand identity and user interface, as well as providing users with a similar look and feel, no matter the device they use.
Top 5 Cross-Platform App Frameworks
For those considering cross-platform development, here are five most popular frameworks to explore:

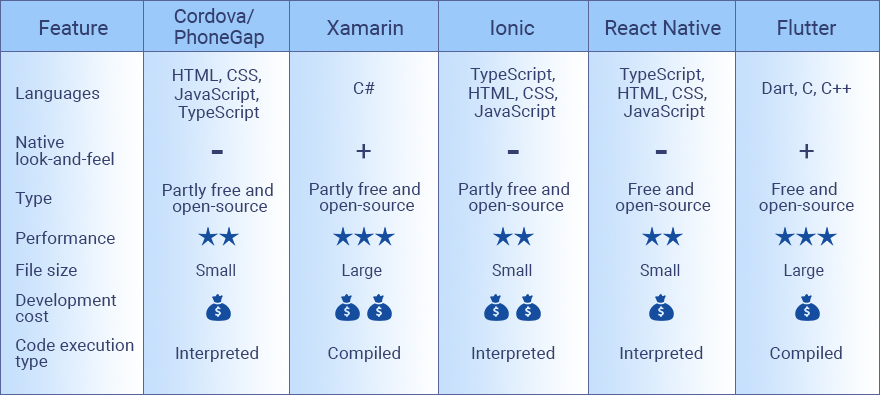
Cordova/PhoneGap
Apache Cordova and Adobe PhoneGap are usually mentioned together since PhoneGap is Cordova with additional Adobe features. They are open-source, free frameworks (some features of PhoneGap require payment).
In order to use Cordova/PhoneGap, an engineer needs to know a technology stack that is typical for web development: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. These frameworks are good for creating MVPs or simple projects as well as projects with small budgets.
Xamarin
Xamarin is a cross-platform development framework owned by Microsoft. Unlike the previous two, the Xamarin app runs on a device’s hardware instead of a web view. This ensures better performance and UX/UI, as well as provides an opportunity to build sophisticated logic. The Xamarin app is the closest to a native application.
React Native
React Native is one of the most popular frameworks for cross-platform app development. It allows building mobile apps using only JavaScript. It uses the same design as React, letting you compose a rich mobile UI from declarative components.
It’s free, offers ready-to-apply elements, and allows you to preview results right away, thus shortening the developing time. The result is a high-quality, native-like user interface.
Ionic
Ionic is an open-source cross-platform app framework that uses HTML5 for translation. It is very similar to AngularJS in design and structure. It is a good choice when creating native-like hybrid apps as well as progressive web apps.
While apps developed in Ionic look similar to native apps, they perform very similarly to native apps.
Flutter
Flutter is a relatively young (founded in 2017) open-source and cross-platform framework for creating native interfaces. It is based on Dart, an object-oriented programming language that is easy to acquire skills for.
It offers faster development time and allows the creation of a great native-like user interface. It is ideal for minimum viable product development.
Explore these frameworks further and find the best fit for your project needs. Check out this article for a more in-depth comparison and insights into each framework.
What Are the Differences
Let’s now put together the most significant features of Cordova/PhoneGap, Xamarin, Ionic, React Native, and Flutter.
Native vs. Cross-Platform Apps: Making the Best Choice
The choice between native and cross-platform mobile software development should rely on your project’s specific demands, conditions, and priorities.
If performance and a platform-specific user experience are more important, then we suggest you choose native development.
If your top priorities are cost efficiency, faster development, and easier maintenance, a cross-platform approach sounds like the ideal solution.
Nonetheless, remember to carefully evaluate your project’s needs, target audience, and long-term goals before making a decision since choosing the right development approach will greatly impact the success of your mobile app.
No matter which development approach solves your business tasks better, SCAND is here to create the robust software solution you need. Whether you are building a social network, a fintech tool, or an e-commerce platform, our startup app development team ensures a smooth journey from prototype to the App Store launch. Contact us now to get your dream project started.












