Hybrid App Development: Pros and Cons
Building a mobile app has long been among the primary goals for businesses that want to improve their marketing and brand positioning. That’s because millions and millions of people today prefer interacting with online services via mobile apps on the go rather than using bulky desktop computers or laptops. This makes building a custom mobile app a high-value target for companies.
While it’s clear that mobile apps facilitate the process of reaching potential buyers and generating new leads, the issue of which mobile app development approach to use remains open – native, cross-platform, or hybrid. Today, many companies opt for hybrid development as it’s much quicker and cheaper. Yet, they should carefully consider hybrid development to ensure that it fits in well with their business requirements.
In this article, we’ll have a detailed look at what hybrid app development is and the advantages and disadvantages of the hybrid mobile app development approach.
Native vs Hybrid: Difference
Before diving into the hybrid mobile development specifics, let’s define what hybrid development is and how it differs from native mobile app development.

At the beginning of the mobile app development era, most mobile solutions were built natively. This means that they were created to run only on specific platforms and devices with the implementation of specific tools, e.g. Swift and Objective C for iOS development, Java and Kotlin for Android development, and so on.
As the popularity of mobile apps was growing, companies started searching for ways to increase their audience reach while cutting down on the development costs. That’s where hybrid mobile development began to gain momentum.
The hybrid mobile app development is different from the native approach as it involves the use of web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They allow building hybrid mobile apps that can be launched on multiple platforms and devices. There are a number of frameworks and tools that help encapsulate web technologies into a native shell and, therefore, build a solid, native-like hybrid mobile application. They include React Native, Ionic, Flutter, Xamarin, PhoneGap, and many others.
While relying on web technologies, hybrid mobile app developers can include some native elements in their solutions. This means that they can incorporate such native to a specific platform features as geolocation, accelerometer, camera, etc. into their apps, making them more functional and smooth in comparison to web-based only solutions.
Hybrid Apps Benefits and Shortcomings
Hybrid mobile apps combine the technologies of both software development vectors – native mobile and web mobile developments. This results in certain pros and cons inherited from these approaches. Let’s have a closer look at some advantages first before moving to possible shortcomings.

Why Hybrid Apps?
- Functionality. When done well, it’s almost impossible to differentiate a hybrid app from a native since it provides the same authentic, responsive, and simple-to-use experience. Thanks to such frameworks as PhoneGap, Xamarin, and Titanium, developers can build apps using the HTML-CSS-JS bundle. The JS API enables free access to native device capabilities (camera, contacts, geolocation, accelerometer, hardware device buttons, and more).
- Maintenance. Maintaining a native app requires special skills whereas hybrid apps are as simple to maintain as a web page. That’s because the changes are implemented only when they are needed and they don’t require any client app distribution.
- Development costs. Building a hybrid app is much quicker and, therefore, much cheaper in comparison to native apps. That’s because mobile developers write a hybrid mobile app code only once and it’s deployed to multiple platforms. Native apps, in turn, will require building a stand-alone app from scratch for each mobile platform.
- Development cycle. Hybrid apps are developed faster resulting in quicker ‘time-to-market’. Gaining from the multiple options and frameworks reduces the learning curve and allows developers to concentrate on the project requirements more. Moreover, hybrid apps are a great option when a business needs to build an MVP first and test it on several mobile platforms.
- Cloud support. Hybrid apps built with the help of Titanium Ionic or PhoneGap frameworks can be simply integrated into the cloud. This allows software developers to simply upgrade app functionality, fix development or design flaws, or scale the app up/down depending on the current requirements almost instantly.
- Internet requirement. Hybrid apps can effectively function offline and don’t require any constant internet connection. The app will automatically update any changes made offline as soon as it connects to the internet again.
- Security. Good app development practice ensures high-level quality and security. Hybrid apps are supposed to be as secure as native apps. However, if security is among the top priorities, the native approach still handles it better.
Cons of Hybrid Apps
- Performance & Functionality. Since most hybrid apps are built with the help of web technologies, they require way more processing memory and power which can lead to performance degradation. Also, there’s a certain limit of functions, the existence of a non-native interface that looks alike on all platforms, and the necessity of creating various components from scratch instead of using the ones available by default.
- UI/UX. It’s an issue for hybrid apps as they can’t provide a sheer “native” experience. Native apps use user-friendly system interface components that keep the overall workflow whereas hybrid apps can’t achieve it without performance slowdown.
- Maintenance. Since a hybrid app is a web one filled with local containers, to access native features they have to use specialized APIs. Hence, the app capability might be limited as there’s a need to involve third-party tools. Apart from that, mobile platforms have unique features and functions not used on other platforms. This way, to keep the app consistent, mobile developers will have to exclude them from the app feature list. For example, they can be widgets on android or uninterrupted animated graphics on iOS, etc.
Are Hybrid Apps the Future?
As mobile apps keep on growing in importance and the demand for mobile app development services grows along with it, companies are seeking alternative paths to build and deliver high-quality apps for their clients. Speed to market, availability of various resources, and easy updates make the hybrid approach enticing.
Many world-known companies opt for the hybrid mobile development approach when building their custom solutions. These companies successfully operate in the market while largely relying on their mobile apps when providing their services. Some of the most prominent examples include Uber, Gmail, Evernote, Twitter, Instagram, and many others.
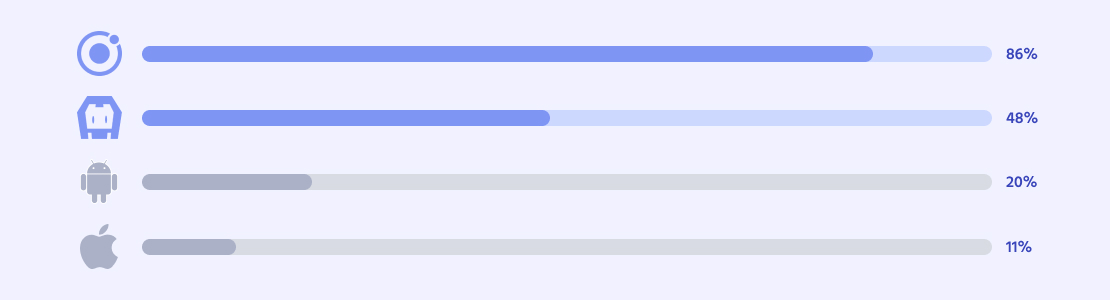
It’s expected that hybrid apps will only grow in their popularity in the upcoming years and this can be backed up by the stats. According to the Ionic Developer Survey as of 2020, such cross-platform and hybrid tools as Ionic (86%), Cordova (48%), Android (20%), and iOS (11%) are used more frequently in mobile app development:
Meanwhile, the tendency of growing popularity for cross-platform and hybrid tools can also be tracked in Stack Overflow reports 2021/2022. For example, Flutter and React Native remain among the top most wanted technologies to learn whereas Xamarin keeps growing in popularity, reaching 5.21% in 2022 in comparison to 3.9% recorded in the Stack Overflow report of 2021.
Who Would Benefit from Hybrid Apps?
The decision of choosing hybrid mobile development should come from the business requirements of a particular company. Nevertheless, this type of development is rather popular among small and medium-sized businesses that don’t require high app performance.
Also, building a hybrid app is a good choice for start-ups due to its fast development, simple server communication, improved compatibility, etc. It’s suitable for products and services focusing on content and local purposes.
As for large-sized companies, developing a hybrid solution might be a nice decision for creating an MVP. For example, if the company is releasing a new product or service and yet it’s not clear whether people need that, a hybrid approach will come in handy to test this hypothesis with the help of quick MVP development.
Conclusion
More and more companies today build custom mobile applications to reach their audiences better and provide their services more effectively. Many of them turn to hybrid mobile development as it allows developing a mobile solution quicker and for a lesser amount in comparison to native mobile software.
While the hybrid app development approach offers a wide range of advantages, companies still have to consider whether it suits their business requirements well. Once you’re sure that hybrid development is the right option for your mobile development project, the next step is to find a team of experienced mobile developers. Scand offers teams of professional mobile software developers that can help you build a solid, secure, and performant hybrid solution. Contact us to find out more about hybrid app development.












