Best Liquidity Pools in Crypto: How to Choose & Earn Big in 2025
If you choose high-volume, well-vetted pools with incentives, wisely manage impermanent loss, and diversify your positions, providing liquidity can be an attractive source of passive income in the DeFi ecosystem. However, it’s not without risk: you need to understand the mechanisms, carefully select your positions, and closely monitor them.
DeFi describes financial services created on and operated via blockchain. It’s an already impactful market (with a total amount of $14.0 billion) that stands behind lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges, staking, and, of course, trading.
But in the world of DeFi, to support trading activity, the ecosystem relies on liquidity pools. Without pools of tokens locked in smart contracts, DEXs (decentralized exchanges) would lack the depth and responsiveness needed for reasonable swaps.
Total Value Locked (TVL) in liquidity pools has grown year by year as more individuals believe in decentralized markets and realize the worth of providing market liquidity in order to attain minimum slippage, efficient price discovery, and constant trading.
What Are Liquidity Pools: Definition & Purpose
Liquidity pools are one of the foundational inventions of decentralized finance (DeFi). In simple terms, a liquidity pool consists of crypto tokens locked within a smart contract that allows users to trade, lend, or borrow assets without needing intermediaries or order books.
In centralized exchanges (Binance or Coinbase), trades occur when a buyer’s order meets a seller’s order. But in the decentralized domain, there’s no central authority to manage the matching process.
Instead, liquidity pools replace order books with a pool of tokens that are always available for trading. Prices are automatically determined by mathematical formulas known as Automated Market Makers (AMMs) — like the famous x · y = k model pioneered by Uniswap.
People who supply tokens to these pools are called liquidity providers (LPs). They deposit their assets (in pairs, such as ETH and USDC) into a pool for others to trade against.
Each trade in the pool generates fees, a portion of which goes to LPs. Essentially, they act as market makers, providing liquidity in exchange for rewards.
Liquidity pools, by the way, power much more than mere token swaps. They also serve as the backbone for yield farming, decentralized lending, synthetic asset creation, and cross-chain liquidity transfers — making them an indispensable component of nearly every DeFi protocol today.
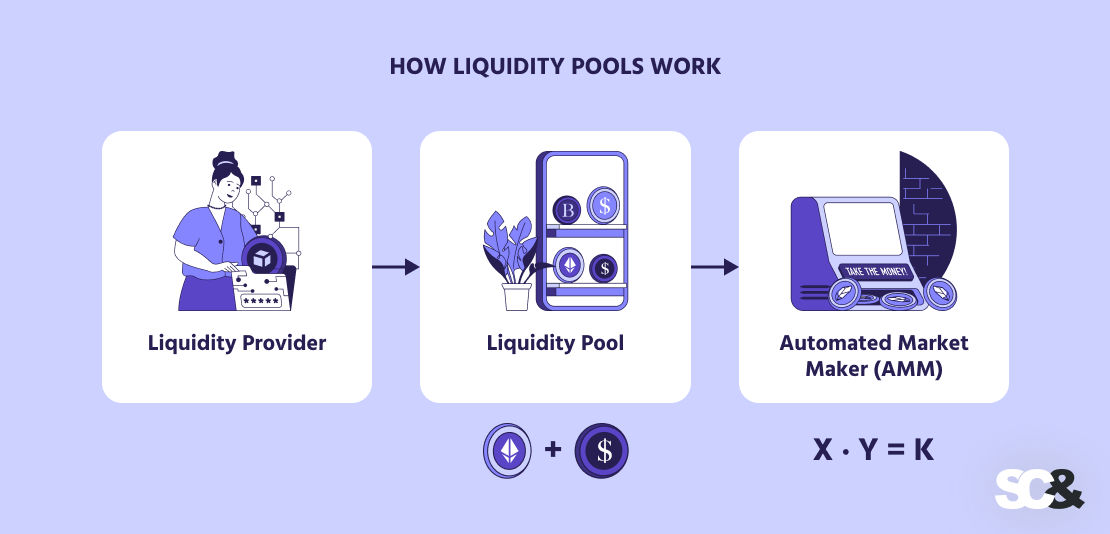
Key Concepts & Mechanics
Now that we’ve covered what decentralized liquidity pools are, let’s talk about how they actually work and what key concepts you should know before getting started with one.
LP Tokens (Share Representation)
When you deposit tokens into a liquidity pool, you get LP tokens in return that represent your share of the pool. When you decide to withdraw your money, you’ll swap out your LP tokens for your share of the pool assets, as well as for any trading fees you earned in the process.
Earning Fees
Every time a user swaps tokens through a pool, they pay a small trading commission (e.g., 0.3%). That fee doesn’t go to the platform — it’s divided between all the liquidity providers. So, the more trades that happen in a pool and the larger your share, the more you earn.
Impermanent Loss
One of the most important things to understand is impermanent loss. It happens when the prices of the tokens in your pool change compared to when you first added them.
Because AMMs automatically rebalance the pool, you might end up with more of one token and less of the other — and that can sometimes leave you with less value than if you had just held the tokens separately.
The loss is “impermanent” in the sense that it can disappear if prices return to where they started, but it becomes permanent the moment you withdraw.
For example:
- Suppose you deposit 1 ETH and 1,000 USDC (ETH = 1,000 USDC) into a 50/50 pool.
- If ETH doubles in price to 2,000 USDC, arbitrage adjusts the pool so that you end up with ~0.707 ETH + ~1,414 USDC, worth ~$2,828 total.
- But if you had held 1 ETH + 1,000 USDC, the total would be $3,000.
- That ~$172 difference is an impermanent loss.
Single-Sided vs. Dual Token Provision
Traditionally, pools require you to deposit two tokens of comparable value (such as ETH and USDC). This is called dual-token provision.
Some newer platforms, however, now provide single-sided staking, where you can stake one type of token alone. These pools handle the pairing on their own, making the process simpler, though often with slightly different risks or rewards.
Types of Liquidity Pools & AMM Models
Not all liquidity pools work the same way. Different DeFi platforms use different AMM models. Understanding these models allows you to choose pools most appropriate for your goals and risk tolerance.

Constant Product (x · y = k): The Classic Model
Constant product is the most common AMM formula, suggested by Uniswap. It keeps the product of two token reserves (x and y) equal to a constant value (k).
Simply put, when one token is purchased, the price adjusts automatically according to how much is remaining in the pool. This is an ideal model for most pairs of tokens, but it will lead to greater price slippage when there are massive trades or there is little liquidity.
StableSwap: Low Slippage for Stable Assets
Used by Curve Finance, this model is perfect for trading assets that stay close to each other in price, such as stablecoins (USDC, USDT, DAI). The formula reduces slippage and impermanent loss, which makes it ideal for stable or pegged tokens.
You will not get wild yields here, but the returns are steady and the risk is visibly lower.
Concentrated Liquidity (Uniswap v3 style)
Popularized by Uniswap v3, concentrated liquidity lets LPs choose specific price ranges where they want to provide liquidity instead of spreading it across all prices.
This type increases capital efficiency, meaning you can earn more with less capital, but if the price moves outside your chosen range, your funds will stop generating income until the price returns to normal levels.
Multi-Asset Pools: Beyond Token Pairs
Some platforms (for instance, Balancer) allow more than two tokens in a pool (for example, 80% ETH + 10% WBTC + 10% USDC). These multi-token pools provide more diversification in portfolio management.
LPs can hold different weights of tokens instead of the same 50/50 percentage, adjusting their exposure to the market.
Synthetic or Derivative Pools
Some pools use synthetic assets — tokens that represent other assets or mirror their value (e.g., synthetic USD or wrapped Bitcoin). These pools allow users to trade derivatives or gain exposure to assets from other blockchains, with more potential for yield but also higher risk.
What Makes a Liquidity Pool “Good”?
With thousands of liquidity pools available across different blockchains, they aren’t all worth your while — or your tokens. A “good” liquidity pool offers a balance between profitability, safety, and usability. Here’s what to look at before deciding where to put your funds.
Liquidity & Depth
The total value locked shows the total amount of funds in a pool. Larger TVL generally means deeper liquidity, which reduces slippage — the price movement that happens when large trades move the market.
Deep pools are more stable, while shallow ones can create extreme price swings and higher risk for LPs.
Trading Volume & Fee Yield
A pool that’s actively traded generates more fee income for its providers. The best pools combine strong liquidity with steady trading volume.
Each swap in the pool incurs a small fee (often between 0.05% and 0.3%), which gets distributed among LPs. The more trading volume in a pool, the higher your reward.
Rewards & Incentives
Many DeFi protocols attract crypto liquidity providers by offering additional rewards, such as governance tokens or bonus emissions, in addition to trading fees.
However, it’s important to check the emissions schedule — certain rewards taper over time or require you to lock up your money for longer periods.
Risk Factors
Liquidity pools carry a few risks you shouldn’t ignore:
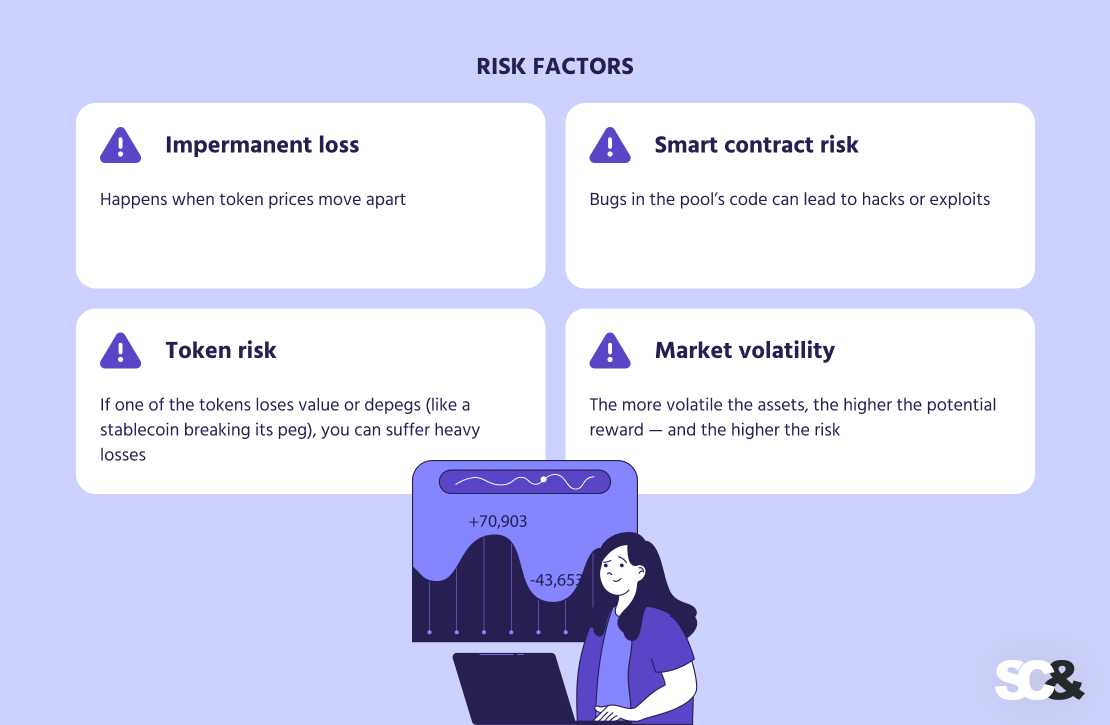
- Impermanent loss: Happens when token prices move apart.
- Smart contract risk: Bugs in the pool’s code can lead to hacks or exploits.
- Token risk: If one of the tokens loses value or depegs (like a stablecoin breaking its peg), you can suffer heavy losses.
- Market volatility: The more volatile the assets, the higher the potential reward — and the higher the risk.
Capital Efficiency & Flexibility
Some AMMs, like Uniswap v3 or Curve, let you focus liquidity on specific price ranges, increasing capital efficiency (earning more with less capital). Others allow flexible pool weights or automated rebalancing to help maintain your desired exposure without constant manual adjustments.
Usability & Accessibility
Regardless of how lucrative the pool is, if it is not easy to use, it doesn’t matter. Look for platforms with:
- Low gas fees or availability on Layer 2 networks.
- Simple and fully supportive interfaces that make it easy to deposit and withdraw.
- Cross-chain functionality, where you can switch liquidity between ecosystems without complex bridging.
Top Liquidity Pools / Platforms to Consider
Let’s look at some well-known crypto exchanges to better understand how cryptocurrency liquidity pools work. This list is drawn up based on strength, yield potential, and risk profile:
Uniswap (Ethereum / Layer 2s / v3 and newer)
Uniswap remains one of the most popular decentralized exchanges for liquidity provision. It presented the constant product model (x·y = k) and later moved on to concentrated liquidity with Uniswap v3, which gave providers greater control of their capital efficiency.
- Pros: Mature ecosystem, high liquidity, plenty of yield pairs; with concentrated liquidity, it is more capital-efficient.
- Risks: Gas cost on Ethereum, range risk if price moves outside your band.
Curve Finance
Curve is suited for pegged and stable assets such as USDC, USDT, and DAI. Its StableSwap protocol minimizes slippage and impermanent loss, and hence it is most appropriate for investors looking for low-risk and stable yield.
- Pros: Extremely low stablecoin pool slippage, very low impermanent loss.
- Risks: Lower yields unless augmented with further incentives.
Balancer
Balancer has strong support for multi-asset and customizable pool structures. It allows you to create pools with up to eight tokens and assign custom weights (e.g., 80/20 instead of 50/50), which makes it perfect for users who want to build portfolio-like liquidity strategies.
- Pros: Flexible weightings, multiple tokens per pool, good diversification opportunities.
- Risks: More complex mechanics, potentially thinner liquidity in niche pools.
PancakeSwap / BNB Chain pools
As the top DEX on BNB Smart Chain (BSC), PancakeSwap offers fast, low-cost trading and a wide variety of farming opportunities. Its high liquidity and uncomplicated interface make it one of the best platforms for beginners.
- Pros: Lower gas costs, many incentive programs, good for BNB ecosystem users.
- Risks: Higher token risk, less mature security record for some projects.
How to Choose the Right Pool for You
Choosing the right liquidity pool is a trade-off between risk and gain. Although high APYs may be tempting, the best course of action is to match your choices with your goals and risk tolerance.
Start by assessing your risk tolerance. Low-volatility stablecoin pools like USDC, DAI, or USDT yield consistent returns with minimal impermanent loss, but riskier trading pairs like ETH/USDC or BTC/ETH can yield higher fees at the expense of greater risk.
Next, diversify both between pools and platforms to reduce the exposure in the event of a token or protocol failure. For example, split your funds between a stablecoin pool on Curve, an ETH pool on Uniswap, and a small portion in a yield farm for extra incentives.
Also, begin with a small investment and watch performance. Use analytics tools like DefiLlama, Zapper, or Uniswap Info to track TVL, trading volume, and fees.
Check the platform’s security and reputation. Established protocols, such as Uniswap, Curve, and Balancer, offer audits and active communities, while newer pools can be riskier.
Lastly, prepare an exit strategy. Don’t be afraid of withdrawing when conditions change, and be ready to move funds to better-performing pools.
Step-by-Step: How to Join & Earn
Frankly speaking, joining a liquidity pool is easy, but it does require a basic understanding of how DeFi platforms work and taking some precautions to guarantee the security of your assets.
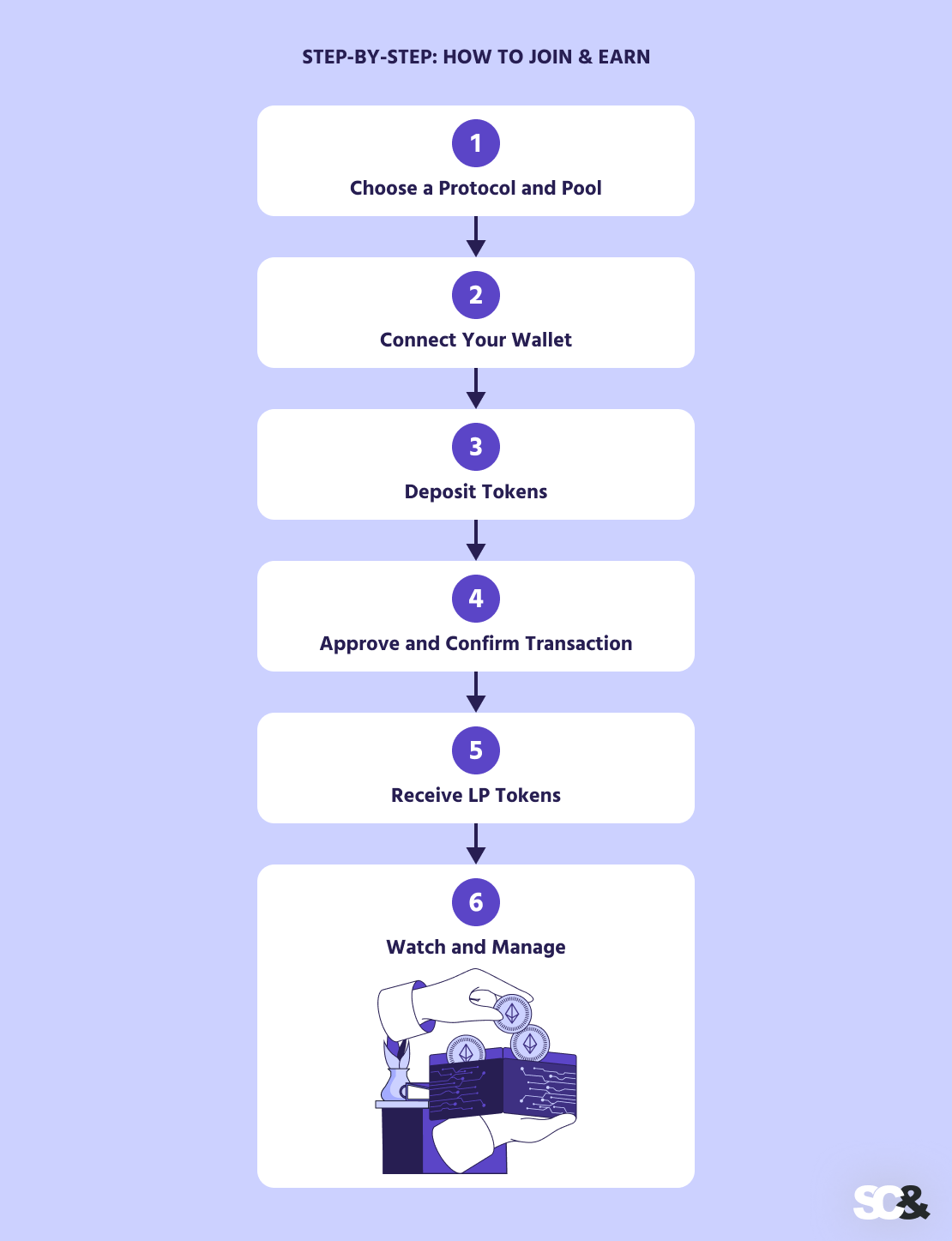
By providing liquidity, you contribute to the protocol’s trading ecosystem and, in turn, receive a share of fees or additional incentives.
- Choose a Protocol and Pool: Start by selecting a reputable platform and a pool that goes in line with your goals, be it a stablecoin pair for lower risk or a volatile pair for higher rewards.
- Connect Your Wallet: Use a crypto wallet to connect to the platform. Make sure your wallet has enough of the tokens required for the pool.
- Deposit Tokens: Deposit the matching token amounts to the pool. Pools generally require equal value for every token (e.g., 1 ETH + 1,500 USDC), though certain pools offer single-sided deposits.
- Approve and Confirm Transaction: Approve the smart contract to access your tokens and confirm the transaction. This may involve paying a network fee (gas).
- Receive LP Tokens: Once your deposit is confirmed, you’ll receive LP tokens representing your share of the pool. The tokens entitle you to a share of trading fees and any rewards.
- Watch and Manage: Regularly check your position for fees earned, impermanent loss, and reward distribution. Use analytics dashboards to follow performance and decide when to withdraw or move funds.
How SCAND Can Help
In DeFi, one small coding mistake can amount to huge losses. Bugs, security vulnerabilities, or unaudited smart contracts have already cost the industry billions of dollars, which is why quality smart contract development and audits are so important.
At SCAND, we help DeFi platforms, liquidity providers, and blockchain startups secure their systems with end-to-end smart contract development, auditing, and testing. Our blockchain engineers and security professionals thoroughly vet every detail of your contract — logic, performance, compliance — to make sure everything works the way you want it to before deployment.
We don’t only detect defects. Our team also rewrites your contracts to make them more optimized, less costly to perform (gas-efficient), and easier to update in the long run.
We balance automated and human testing to detect vulnerabilities, such as reentrancy attacks, logic errors, or poor access controls that are usually attacked by hackers.
If you’re creating your own AMM, liquidity pool, or DeFi app, we can even create custom smart contracts for you — from liquidity and dynamic fee management to designing staking or token reward systems.
Advanced Strategies & Tips
After you have mastered the basics of liquidity provision, there are some advanced strategies you can experiment with to compound returns and limit risk.
One of these strategies is pool hopping and liquidity migration. Moving funds from lower volume or lower-yielding pools to more performing ones can optimize returns, and some platforms promote this without cashing out.
Then, you can use the LP tokens as collateral to borrow other assets. This enables you to borrow while your tokens are still generating fees in the pool.
For instance, you could use borrowed tokens to invest in another pool or opportunity without removing your initial deposit — basically putting your money to work in two places at once.
One alternative is to utilize Yearn or Convex crypto liquidity solutions. They automatically transfer your funds from one pool to another, claim rewards, and reinvest them in order to maximize your total yield.
It’s as if you have a smart assistant that manages your liquidity so that you do not have to manually monitor everything.
You can also try cross-chain strategies, where you split your capital over different blockchains. This way, you get to access pools with better rewards or lower fees. Bridging assets between chains does come with some risk, however, so only use trusted and secure bridges.
Finally, experienced users employ hedging and rebalancing to protect their capital. For example, you can split your investment between stablecoin pools (less risky) and volatile pools (more rewarding).
Common Mistakes & Pitfalls to Avoid
DeFi liquidity provision is profitable, yet not risk-free. A majority of investors commit fundamental mistakes that can cost them money if they do not take measures.
One of the easiest mistakes is ignoring gas and transaction fees. Transaction fees on a network like Ethereum are not negligible and can eat into your profits in case your investment is small.
Another trap is failing to account for impermanent loss. Even after earning fees, token price volatility can minimize your net profit. In this way, it’s great to be aware of this risk and check your pool regularly.
Others put all of their money in new or risky pools. This approach is always reckless because new or unaudited protocols can either get hacked or tokens can become worthless overnight.
Chasing very high returns without consideration of the risks is also prevalent. High returns are typically preceded by high volatility or illiquid markets.
Lastly, not having a withdrawal strategy can be detrimental to your gains. Providing liquidity is not “set and forget.” It is being aware of when to withdraw your funds and when to transfer them to more promising opportunities to safeguard your funds.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a liquidity pool?
A liquidity pool is a collection of crypto tokens that are pooled and locked in a smart contract, which people may trade, lend, or borrow against. If you contribute tokens to the pool as a crypto liquidity provider, you get a share of the trading fees.
How do I earn from liquidity pools?
Usually, you are rewarded for staking tokens in a pool. A small fee is taken each time a trade is executed and shared with all LPs. Pools also exist with added rewards, such as governance tokens or bonus yield farming.
What is impermanent loss?
Impermanent loss is when the price of tokens in the pool changes after you deposit them. Such a change in price reduces your overall return if you had just kept the tokens. The loss remains permanent only when you cash out your money.
What are LP tokens?
Essentially, LP tokens are your portion of the pool. They help you get your share of assets and any withdrawal fees when you withdraw. You can even stake LP tokens in some pools and get extra rewards.
Which pools are safest for beginners?
Usually, the safest pools are the stablecoin pools, such as USDC/DAI or USDT/USDC. They have low volatility, minimal impermanent loss, and steady returns.
How do I choose the best pool?
First of all, look at total value locked, trading volume, fees, rewards, and risk. In practice, you can spread your funds across different pools, start small, and use analytics tools to watch performance.
Can I lose money in a liquidity pool?
Yes. As with the entire crypto market in general, there are certain risks. Regarding liquidity pools, these include impermanent loss, token price swings, smart contract defects, or project failures.
How do I get started?
Getting started is pretty simple. Pick a trusted platform and pool, connect your wallet, deposit your tokens, get LP tokens, and optionally stake them for extra rewards.












