All About Blockchain in Payments: How It’s Transforming Transactions
Online payments and fintech inventions have demonstrated remarkable metamorphosis in the past five to ten years.
Cheques and cash have been almost completely replaced by mobile wallets and digital banking, and what once required a trip to the bank can now be done with a few taps on a smartphone.
There are disagreements in 2025, however, on whether this growth will continue or decelerate. Crisis, regulation, and sustainability challenges to financial services all impact the payments industry in 2025.
There are several options and ways of influencing the situation, bold and humble. In the last few years, the most likely contender for the role of an online payment instrument has been blockchain technology.
What Is Blockchain Technology in Payments?
In essence, blockchain is a digital ledger that’s shared across a network of computers. Instead of having to involve a bank or payment gateway to exchange money, blockchain lets a set of users group together and confirm the transaction.
This way, you don’t have a middleman involved, which saves money and time, and makes the whole process more transparent.
Normally, sending money abroad takes days and gets routed through various banks. On blockchain, the exact same transfer can be conducted in a matter of seconds, with much fewer charges and much less hassle.
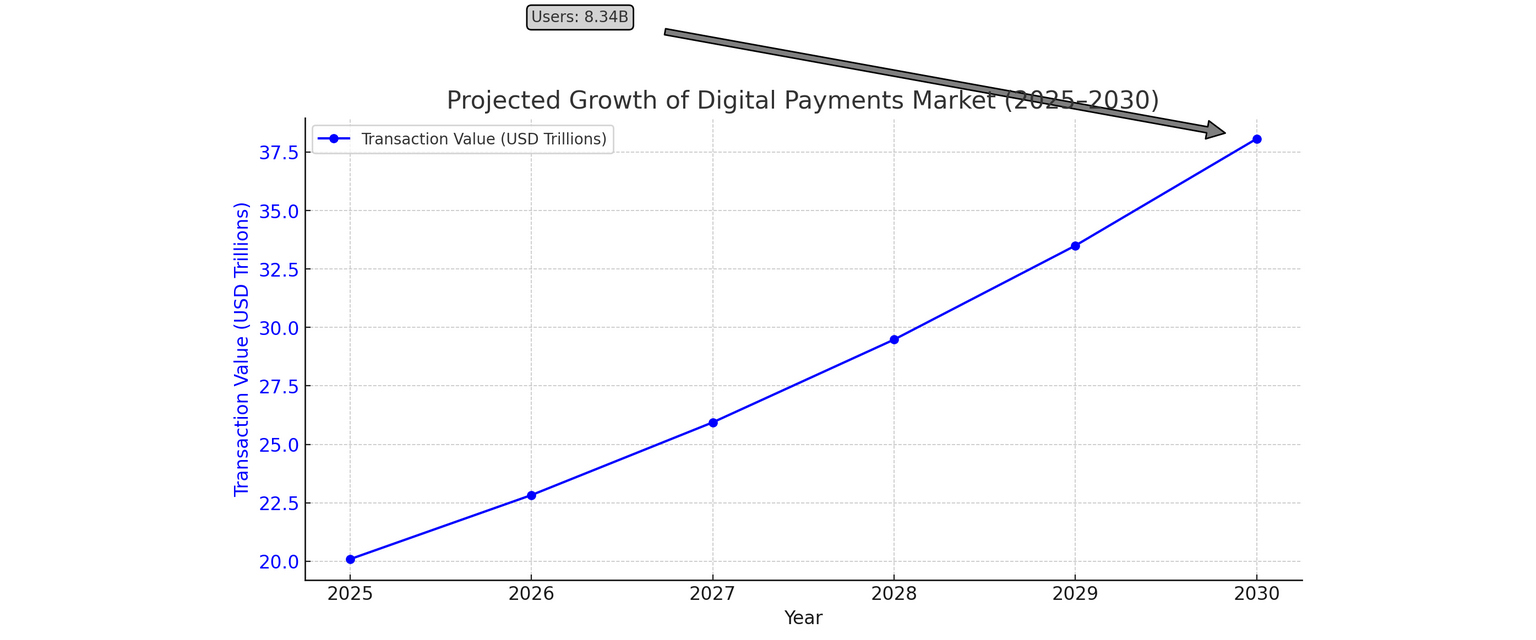
Projected Growth of Digital Payments Market (2025–2030)
Key Benefits of Using Blockchain in Payments
Blockchain is getting a lot of attention in the world of payments, and for good reason. It solves many of the problems we’re used to dealing with when sending or receiving money.
First of all, cross-border payments and old-fashioned payments can take days to settle. With blockchain, on the contrary, the same financial transaction may be settled in minutes or seconds. That’s a huge difference, especially for people or businesses that need money to move quickly.
Second, regular bank transfers often incur additional fees, possibly from multiple banks that handle the transaction. Blockchain, in turn, cuts out middlemen, saving users’ money on each operation.
The next huge benefit is transparency. All blockchain transactions are placed into a public record book that can’t be manipulated. So everyone can see what’s happening and can be certain the information is accurate.
And unlike banks, blockchain doesn’t respect weekends. Payments go out or come in 24/7 without regard to time or day. Neither does it require a traditional bank account, so those without access to banking facilities can still utilize it to send and receive money.
Short and sweet, blockchain payments are faster, cheaper, more secure, and more flexible compared to a lot of what exists today. It’s an emerging technology, but already it is providing us with a better means of sending money.
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain-Based Payments |
| Speed | 1–5 days (cross-border) | Seconds to minutes |
| Fees | 3–7% | Often less than 1% |
| Transparency | Low | High |
| Availability | Bank hours | 24/7/365 |
| Security | Centralized, breach-prone | Decentralized, encrypted |
| Trust Model | Third-party institutions | Distributed consensus |
Blockchain vs. Traditional Payment Systems: A Comparison
Types of Blockchain-Based Payment Systems
In the year 2023, central banks globally were uncertain about the long-term position of blockchain in international payments.
However, as of 2025, blockchain opens up more than one channel to send money. Depending upon requirements, businesses can choose the type of blockchain-based payment system that fits best.
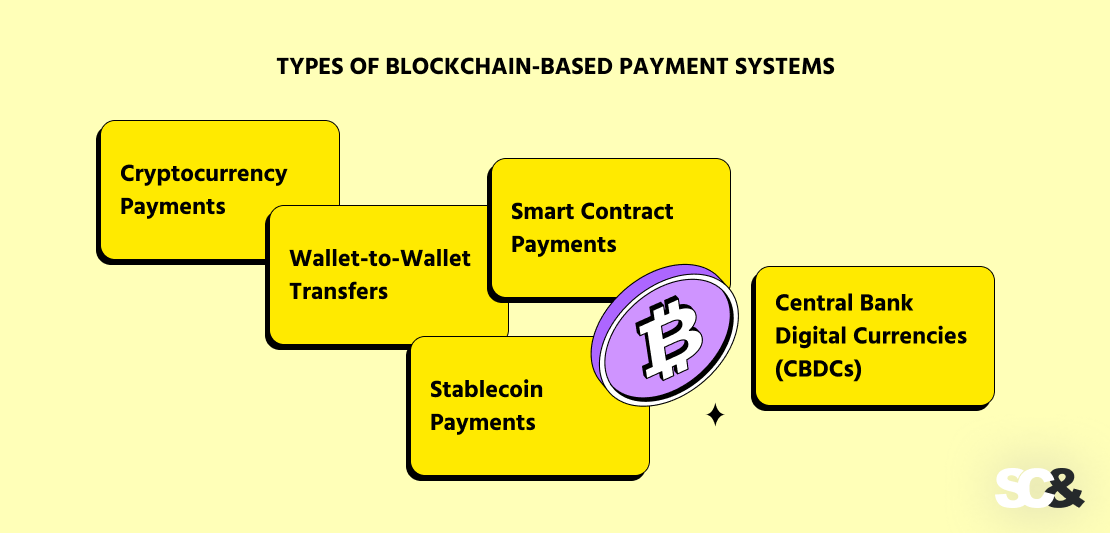
1. Cryptocurrency Payments
This is the classic one. People pay using digital currencies, such as Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), or stablecoins like USDT or USDC. Overall, cryptocurrency payments are great for reaching global users, especially in territories with inflexible banking services.
2. Wallet-to-Wallet Transfers
The wallet-to-wallet type is a direct transaction between two blockchain wallets. One person sends money to another person without using banks or intermediaries. It can be done through scanning a QR code or copying a wallet address.
In general, it’s a great fit for marketplaces, tipping features, donations, or apps where customers pay each other (like ride-sharing, freelance, or content creation apps).
3. Smart Contract Payments
Smart contracts are self-executing programs that run on the blockchain. They automatically send payments when certain conditions are met — no one has to press a button.
By and large, smart contracts are useful for automating milestone-based freelancer payouts, subscription renewals, or revenue splits. Once set up, they run on their own and reduce manual work.
4. Stablecoin Payments
Stablecoins are digital assets tied to real money (for example, the US dollar) and are therefore less volatile than Bitcoin or Ethereum.
This way, stablecoin payments are a good option to utilize if you require fast, inexpensive transfers without the volatility risk of price changes, such as cross-border payrolls, supplier payments, or subscription invoices.
5. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
CBDCs are digital versions of government-issued money, such as a dollar or euro. Some countries are already experimenting with them, and many states are expecting them to replace cash.
As believed, CBDCs can offer the speed of blockchain payments with the legal backing of central banks. If you’re in a regulated industry or deal with government clients, this is something worth waiting for.
How the Blockchain Payment Process Works: Step-by-Step
Making a blockchain payment might sound too technical, but under the hood, it’s just a series of actions that all happen pretty quickly.

If you’re considering adding a blockchain-powered payment system to your app, platform, or service, it’s good to understand what’s happening and what it means for your business operations.
1. A User Makes a Payment
Normally, the process starts with a user — a shopper checking out, a freelancer getting paid, or a business-to-business invoice. They open their digital wallet, enter the address of the recipient, determine how much to send, and click “send.”
For businesses: You can integrate a wallet directly into your application or connect to popular ones like MetaMask or Coinbase Wallet. The thought here is to make it as seamless as possible for your users to send payments.
2. The Transaction Goes to the Network
Once the payment is sent, the transaction is broadcast to the blockchain network. It’s picked up by a network of computers (nodes) which ensure it’s valid, for example, that the sender actually has the funds.
For companies: Your app will usually use a service like Infura or Alchemy to broadcast this transaction and follow it. You don’t need to host a blockchain server yourself unless you need full control.
3. The Network Confirms It
The transaction is then picked up and confirmed. This can take seconds or minutes, depending on the blockchain. The network confirms the payment using its built-in verification process (this could be “proof of work,” “proof of stake,” or something else).
For businesses: Choosing the right blockchain is important here. Some are less expensive and quicker than others. If you need quick payments (e.g., at checkout), look into blockchains like Solana, Polygon, or Stellar.
4. The Payment Is Added to the Distributed Ledger
When verified, the transaction is put into a new block, and that block is appended to the blockchain. Now the payment is secured and can’t be changed. It’s permanent and traceable.
For businesses: This is where blockchain really makes a deal. You have a secure, tamper-proof record of payment. You can also trigger automatic actions (like shipping a product or updating a database) when payment is made.
5. The Recipient Gets the Money
The company or person you paid will have the funds in their wallet as soon as the network confirms it. Depending on the blockchain you’re on, this can be almost instantaneous.
For businesses: You can use this confirmation as a trigger to send a receipt, activate a subscription, unlock content, or release an order. It’s all programmable, time-saving, and minimizes errors.
Optional: Real-Time Tracking
You can also give users real-time status on their transaction, just like you would track a package. This builds trust and keeps users informed.
For businesses: Most apps use APIs or libraries (like Web3.js or Ethers.js) to check whether a transaction is pending, confirmed, or failed. You can even show links to blockchain explorers like Etherscan for extra transparency.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Payments
Again in 2023, about one in four interviewees believed blockchain would have an eventual footprint. 15% of interviewees acknowledged only domestic uses of blockchain payments, versus 13% believing in cross-border applications.
Practically, blockchain payments are already being used in a wide range of industries and real-world situations, helping fix pain points that have existed in finance for years.
1. Sending Money Across Borders (Remittances)
Sending money overseas through a bank or money transfer business costs days and a fortune in fees. Frequently, several banks are used along the way, each charging its own fee.
Using blockchain, the same money is transmitted in minutes, without middlemen. The fees are generally much less, too.
2. Buying Stuff Online or In-Store
More and more online stores (and even some diners) accept crypto as a payment option. Buyers can pay with Bitcoin, Ethereum, or stablecoins like USDT or USDC, and the store gets paid either in crypto or automatically converted into regular currency.
Such an option actually has many benefits for stores, such as:
- No chargeback or credit card fraud
- Lower transaction fees compared to banks or payment systems
- Faster access to your money
3. Business-to-Business (B2B) Payments
Blockchain also enables companies to pay each other for a whole range of things, such as bulk orders, invoices, and payments between subsidiaries of a company located in different countries.

Smart contracts can pay automatically upon satisfaction of certain conditions, e.g., upon delivery verification.
For example, JPMorgan’s JPM Coin allows businesses to transfer funds in real time across their own network.
4. Tiny Payments for Content and Streaming
With conventional payment systems, it’s not worthwhile to send very small payments (like a few pennies) because the fees are normally too high. But blockchain makes “micropayments” more feasible and cheap.
This way is great for:
- Tipping housekeepers
- Paying per second of music or video streamed
- Paying per article read or per click
5. Freelance & Gig Worker Payments
Freelancers, remote workers, and gig workers must wait days at times to get paid, especially if they are outside the country. And banks get to take high margins and fees with exchange rates.
Blockchain payments address this limitation by enabling companies to pay directly into an employee’s wallet, nearly instantly and with no ridiculous fees.
For instance, Sablier allows its employers to “stream” payments in real-time so someone can get paid minute-by-minute.
6. Charities & Aid Distribution
Blockchain adds more clarity to donations. Donors can see exactly where their money is going, and charities can guarantee that the money is being used as it was meant to be.
It also works in times of crisis, when people are in urgent need of help and do not necessarily have access to a bank.
Example: The UN World Food Programme employed blockchain to issue food vouchers to refugees in Jordan.
Challenges in Blockchain Payment Adoption
Blockchain payments, like with any new tech, have a few peculiarities preventing broader adoption.
One of the most prominent challenges is regulation. In some countries, crypto is equivalent to regular cash. In others, it’s taxed like property, or illegal altogether.
That inconsistency makes it hard for people and businesses to know what they can and can’t do. Also, many of the financial regulations don’t quite fit the way blockchain works, so compliance isn’t always manageable.
Then comes the usability factor. Crypto wallets, long wallet addresses, cyber incidents, and private keys can be perplexing to those who are not technically inclined.
If users lose their private keys or accidentally send money to the wrong address, they generally can’t get it back. Until using crypto becomes as simple and safe as using a regular banking app, many people will likely stay away.
Volatility is one more challenge. Cryptocurrencies (no matter whether Bitcoin or some recently issued asset) can fluctuate up or down in price in a split second.
It’s hard to use them for everyday purchases because no one wants to spend $10 on something today only to find that money was actually worth $7 tomorrow. Stablecoins (like USDT or USDC), which are tied to the value of traditional currencies, help with this, but they’re not yet widely accepted.
And finally, there’s adoption. While some companies and online stores are starting to accept crypto, most don’t. Until blockchain payments are accepted by more platforms, apps, and point-of-sale systems, they’ll be more of a niche product than something that people use every day.
How to Build a Blockchain Payment Solution
Want to build your own blockchain payment platform? For exchanging cryptocurrencies between customers, for purchasing it in an online store, or for paying business invoices, it starts with a substantial plan and the right people to execute it.
1. Start with Your Use Case
Prior to starting development, you need to decide what type of payment solution you need. Are you solely interested in peer-to-peer transfers? To enable users to check out with crypto? Or maybe to handle cross-border corporate payments?
Your use case will dictate the rest of the process, from which blockchain to collaborate with to what features and user interface you’ll be required to deliver.
2. Choose the Best Blockchain
Different blockchains have different strengths, so you will want to select the highest quality one that fits your use.
Bitcoin is great for simple transactions, Ethereum is ideal for smart contracts for added functionality, and chains like Solana, Polygon, or BNB Chain offer high speeds and lower fees.
If you are making something for a company or organization, you might even use a private blockchain for more control and confidentiality.
3. Choose a Software Development Firm
Lacking an internal team of experienced blockchain developers, you’ll likely need to contract a software company that specializes in blockchain development.
A good development partner like SCAND will allow you to create an easy-to-use solution, without needing to deal with all the complex technicalities yourself, for example, architecture, wallet integration, smart contracts, security, and testing.
4. Launch, Learn, and Improve
When your platform is ready and fully tested, it’s time to launch. After going live, it’s important to carefully monitor how your system is performing. You (or your software development team) will likely have to make tweaks, fix small bugs, and optimize based on feedback.
Closely monitoring user behavior, transaction rates, and overall system health will let you identify issues early on and keep refining the experience over time.
The Future of Blockchain in Payments
Blockchain is rapidly transitioning from a buzzword to a technology that’s being implemented in everyday payments, and its prospects are encouraging.
More and more, banks and financial institutions are starting to integrate blockchain into their existing systems, which enables them to simplify their processes while still being transparent, fulfilling the necessary regulations and compliance requirements.
In the meantime, decentralized finance (DeFi) is growing by leaps and bounds. These sites allow users to lend, borrow, and send money without the involvement of a bank at all. Early days, but DeFi shows how blockchain has the potential to change the nature of finance.
Stablecoins, cryptocurrencies tied to real-world currencies like the US dollar, are also increasingly a big portion of blockchain payments. Stablecoins combine the fast, inexpensive benefits of crypto with the stable value of traditional money, which makes them perfect for daily use.
And now we’re starting to see AI and payments work together. AI helps with fraud detection, payment tracking, and security upgrades. Paired with blockchain’s transparency, this makes payments both smarter and safer.
Generally speaking, blockchain is no longer something of the future — it’s already changing the way people send, get, and work with money. And at the rate things are moving, it’s only going to be more widespread.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does blockchain assist with payments?
It allows people to send money from one to another directly, bypassing banks and the need for intermediaries. This can be faster, less expensive, and function at any time, even internationally.
Is blockchain for payments safe to use?
Yes! Blockchain has strong security to protect transactions. But do use reputable apps and protect your account details.
What is a stablecoin?
Stablecoins are unique cryptocurrencies fixed to traditional money like the US dollar. They do not change much in value, so they are easier to use for everyday payments.
What is positive about blockchain payments?
From the business side, they're speedier and cheaper than regular payments, and work well between nations, even in areas where banks are tricky to use.
What are the downsides of using blockchain money transfers?
By and large, the most widespread problems are unstable prices (except for stablecoins), unclear regulations, and limited adoption.
Will blockchain substitute normal payments?
No, not just yet. But it's gaining momentum as a potential substitute and will soon augment normal payment systems.