Single-Page Application Vs. Multiple-Page Application
When it comes to web application development, there are two fundamental approaches developers can take. These approaches are single-page applications (SPAs) and multiple-page applications (MPAs).
Each approach offers distinct advantages and considerations that can impact user experience, development complexity, and overall performance.
In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between SPAs and MPAs, shedding light on their peculiarities, pros and cons, and the factors that should influence your decision-making.
What is a single-page application?
A single-page application, as the name suggests, runs on a single web page and does not need multiple page refreshes during user interaction.
Unlike traditional web applications, SPAs leverage dynamic HTML updates and asynchronous data retrieval techniques to enhance performance and create a desktop-like experience within the browser.
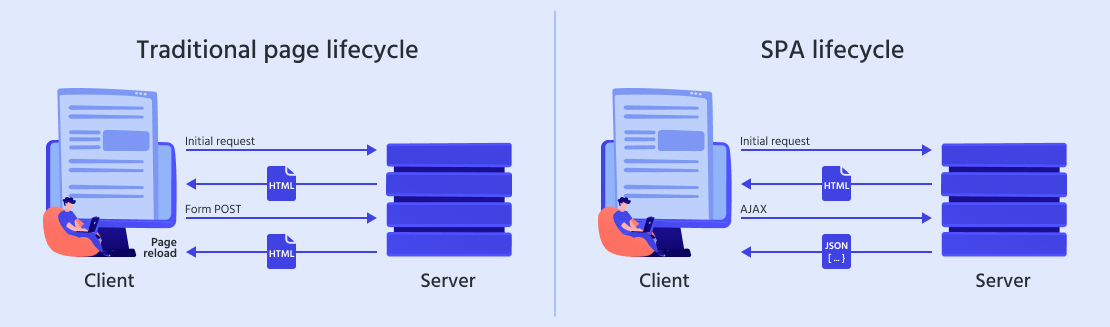
During development, SPAs often utilize JavaScript frameworks or libraries such as React, Angular, or Vue.js. Due to these tools, developers can build complex and interactive SPAs, including social media platforms, email clients, and project management tools.
SPA pros
Single-page applications offer numerous advantages that contribute to their popularity among developers. Let’s explore some major pros of SPAs:
- Enhanced convenience: SPAs offer an incredible level of convenience by delivering a seamless interface that eliminates the need for page reloads. This allows for faster navigation and smoother interactions, similar to using a desktop application.
- Improved performance: By loading resources only once and utilizing asynchronous data retrieval, SPAs reduce the amount of data transferred between the client and server. This results in faster loading and better performance, especially for applications with extensive data volumes or frequent interactions.
- Offline capabilities: SPAs have the remarkable ability to integrate offline experiences through service workers and advanced client-side data storage technologies. This allows users to interact with the app even if they don’t have network access or their network connection is weak.
- Code reusability: SPAs often rely on component-based architectures, allowing developers to reuse code components across different application parts. This promotes code modularity and maintainability and accelerates development speed.
- Cross-platform development: SPAs can run on various platforms, including desktops, mobile devices, and tablets. By leveraging responsive design techniques, SPAs can adapt their layout and user interface to different screen sizes and resolutions.
SPA cons
While SPAs offer numerous advantages, they also come with certain challenges and drawbacks that developers should consider:
- Initial slow loading: Since SPAs load all the necessary resources upfront, the initial loading can be longer compared to MPAs. This can cause a delay before the application becomes fully functional, especially for users with a slower net connection.
- SEO challenges: Search engine crawlers traditionally rely on static HTML content, and SPAs generate content dynamically. And even though search engines have improved the handling of SPAs, developers must implement additional measures to ensure proper indexing and ranking.
- JavaScript dependency: SPAs heavily depend on JavaScript. And if a user disables JavaScript in their browser or has an older device with limited JavaScript support, the application may not function correctly or may not be accessible at all.
- Memory management: SPAs can consume significant amounts of memory, especially when dealing with large datasets or complex user interfaces. This way, developers must carefully use memory and handle its leaks to ensure a smooth user experience.
- Back button and bookmarking: SPAs don’t inherently handle browser navigation features like the back button or bookmarking. Developers must implement additional logic and manage the application state to ensure proper navigation and bookmarking functionality, which can add complexity to the entire development process.
What is a multi-page application?
In contrast to SPAs, MPAs are made up of multiple web pages, where each page represents a different view or functionality of the application.

When a user interacts with an MPA, the browser reloads or navigates to a new page to display the requested content.
MPAs rely on server-side rendering, where the server generates the HTML for each page and sends it to the client upon request. Interactions often involve full-page refreshes, which may result in visual interruptions for the user.
MPA pros
MPAs offer a set of advantages that make them a suitable choice for certain types of applications:
- SEO: MPAs have a more straightforward approach to search engine optimization. Since each page has its own URL and content, search engines can easily crawl and index the pages, improving the application’s visibility in search results.
- Simplicity for small applications: For smaller applications, where each page represents a different view or feature, MPAs can provide a less complex development process that makes it easier to manage the application’s structure and functionality.
- Browser compatibility: MPAs are generally more compatible with browsers and devices, as they rely less on JavaScript for core functionality. This ensures a broader reach and better accessibility for users with older devices or browsers with limited JavaScript support.
- Graceful degradation: In MPAs, if JavaScript fails to load or execute properly, the application’s core functionality can still be accessible. This graceful degradation allows users to navigate and interact with the application, even if certain features are limited or unavailable.
MPA cons
While MPAs have their advantages, they also come with some drawbacks that developers should consider:
- Poor usability: MPAs often require multiple reloads, resulting in a slower and less seamless user experience compared to SPAs.
- Performance impact: In MPAs, each page request incurs additional server round trips and data transfer, which can lead to slower load times.
- Development complexity: Managing multiple pages in an MPA can introduce complexity. Development efforts may be required for navigation, data synchronization, and ensuring a cohesive user experience.
- Limited offline capabilities: Standardly, MPAs lack offline capabilities by default. And as each page requires a network connection for loading, implementing offline functionality for the application becomes a challenging task.
SPA and MPA: What to choose?
When making a decision between SPAs and MPAs, it’s important to consider various factors and evaluate the specific requirements of your web application:
- Development complexity: When it comes to web application development, SPAs are typically a great fit for complex and interactive applications that prioritize a rich user experience and frequent data updates. On the other hand, for simple apps with limited functionality and content, an MPA can be a more suitable solution.
- Efficiency requirements: If productivity and responsiveness are critical for your application, SPAs typically offer better performance compared to MPAs. MPAs, in turn, may have longer loading times, impacting performance and user satisfaction.
- Offline functionality: As stated above, SPAs offer more flexibility in implementing offline capabilities. MPAs, due to their reliance on server-side rendering and full-page refreshes, may have more limited options for such functionality.
- Budget and time constraints: SPAs generally require more initial development time and effort due to their complexity and the need for JavaScript frameworks. MPAs, on the contrary, offer a faster development turnaround and are more cost-effective.
Conclusion
When you need to build a web application, choosing between SPAs and MPAs can be a daunting task.
SPAs offer enhanced user experiences and improved performance but may have longer initial load times, SEO challenges, and knowledge of JavaScript.
On the other hand, MPAs excel in search engine optimization, simplicity for small applications, and browser compatibility but may have performance slowdown and development complexity.
Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all answer, and the ultimate choice between SPA and MPA will depend on various factors.
Carefully consider your finances, goals, and restrictions, and choose the approach that aligns with your project’s needs and delivers a successful web application.












